引言
本博文对基于learning的lidar odometry(包括lidar,lidar+IMU等)进行调研,并对一些经典的工作进行阅读。
本博文仅供本人学习记录用~
- 引言
- Paper List
- 经典工作介绍
- LONet: deep real-time LiDAR odometry
- DMLO: Deep Matching LiDAR Odometry
- Self-supervised Learning of LiDAR Odometry for Robotic Applications
- Efficient 3D Deep LiDAR Odometry
- Translo: A window-based masked point transformer framework for large-scale lidar odometry
- DiffLO: Semantic-Aware LiDAR Odometry with Diffusion-Based Refinement
- Pointconv: Deep convolutional networks on 3d point clouds
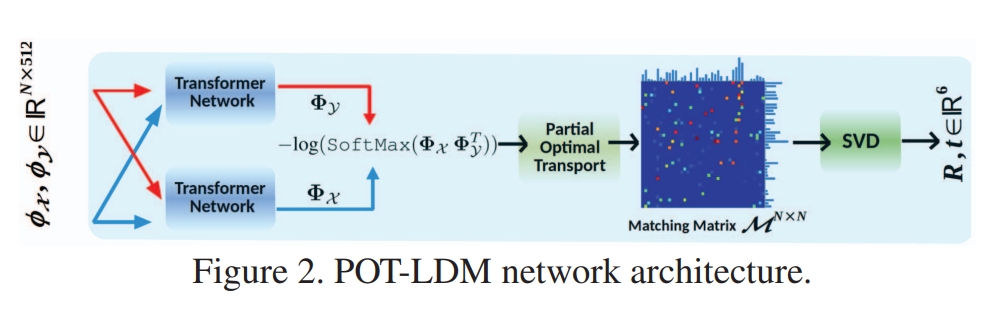
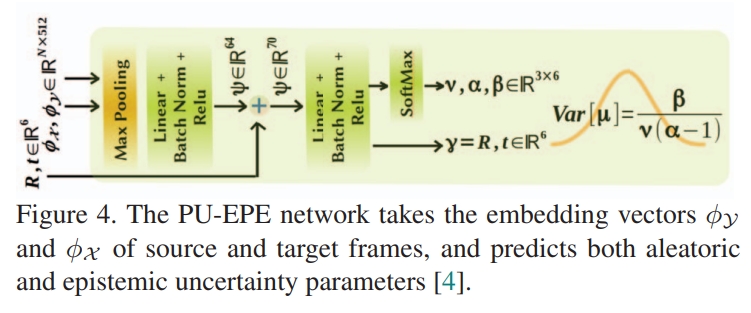
- DELO: Deep Evidential LiDAR Odometry using Partial Optimal Transpor
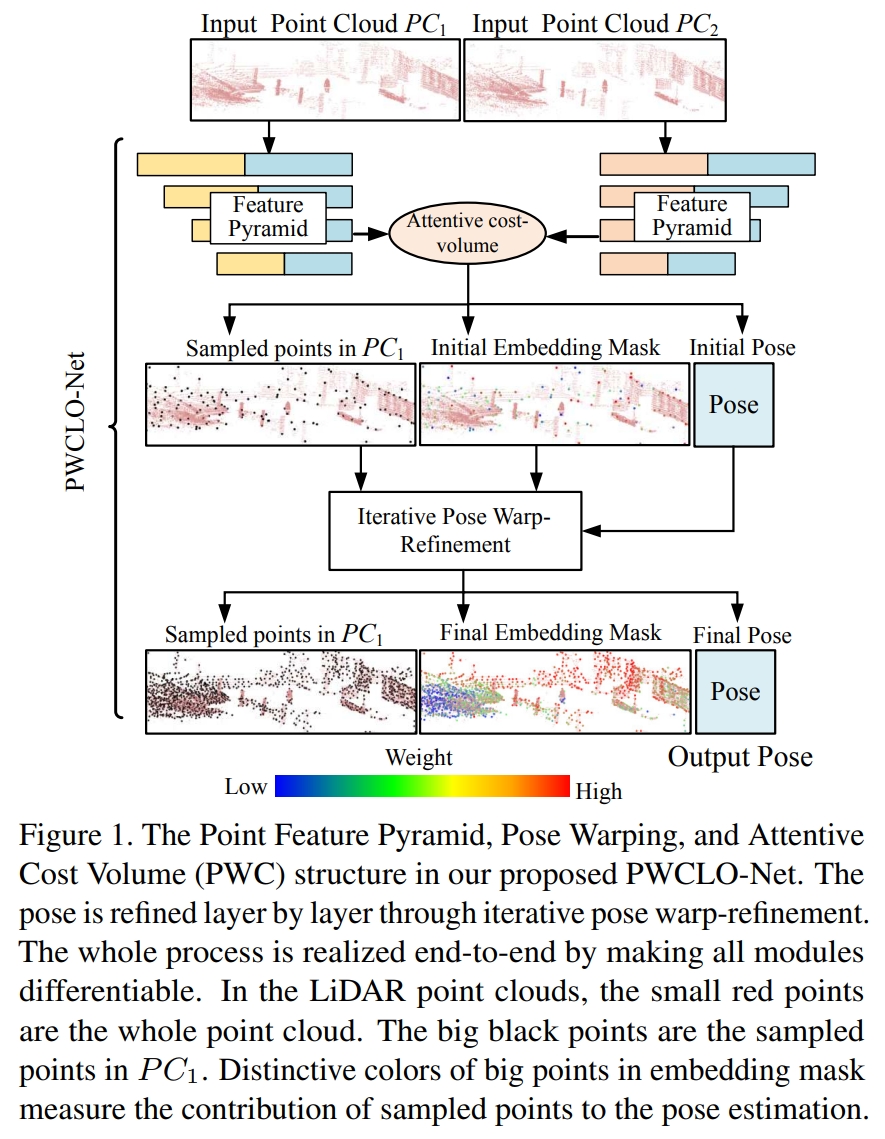
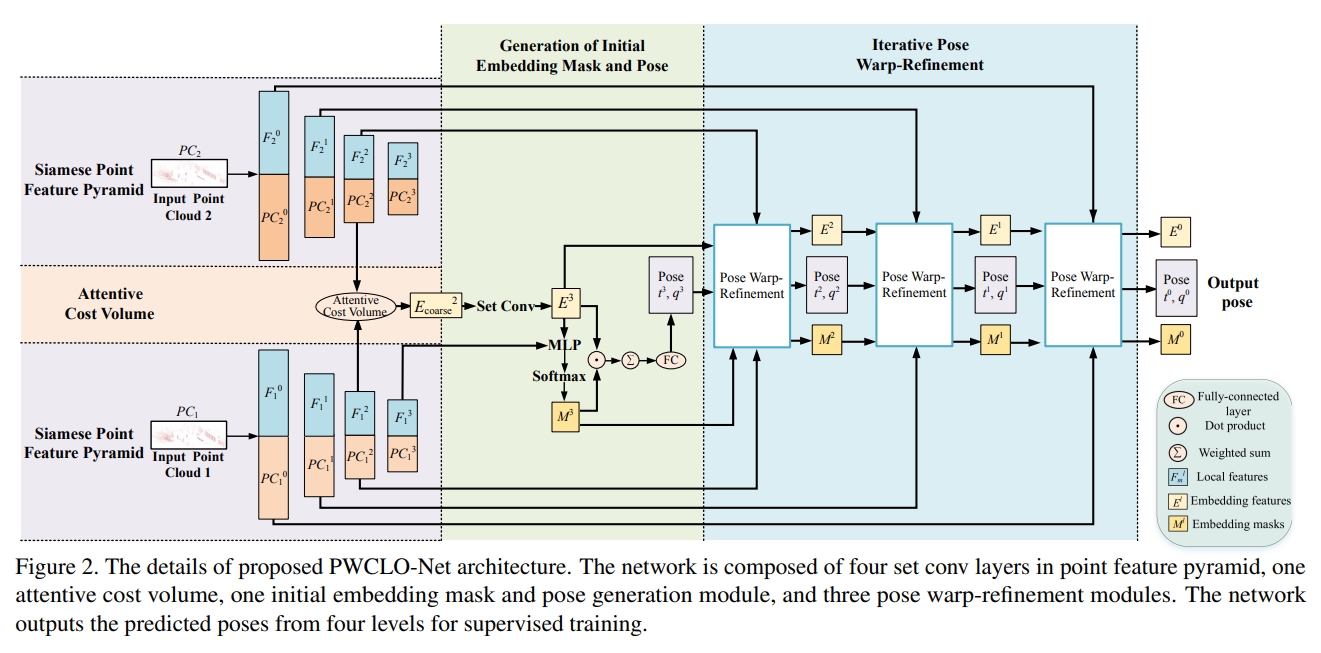
- PWCLO-Net: Deep LiDAR Odometry in 3D Point Clouds Using Hierarchical Embedding Mask Optimization
- Pointnet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space
- A Consistency-Aware Spot-Guided Transformer for Versatile and Hierarchical Point Cloud Registration
- Kpconv: Flexible and deformable convolution for point clouds
Paper List
- 其他有代表性的基于learning的lidar工作或者point cloud registration:
经典工作介绍
对于基于learning的lidar odometry主要有以下几个挑战:
- 两帧离散的lidar scans如何建立准确的数据关联
- 由于遮挡或者lidar的分辨率限制而导致的,属于同一个物体的点云,在两帧中不一致
- 动态点云
- 直接从原始3D点云学数据通常是低效的(由于点云的不规则及无序性),也就是如何获取更好的representation learning
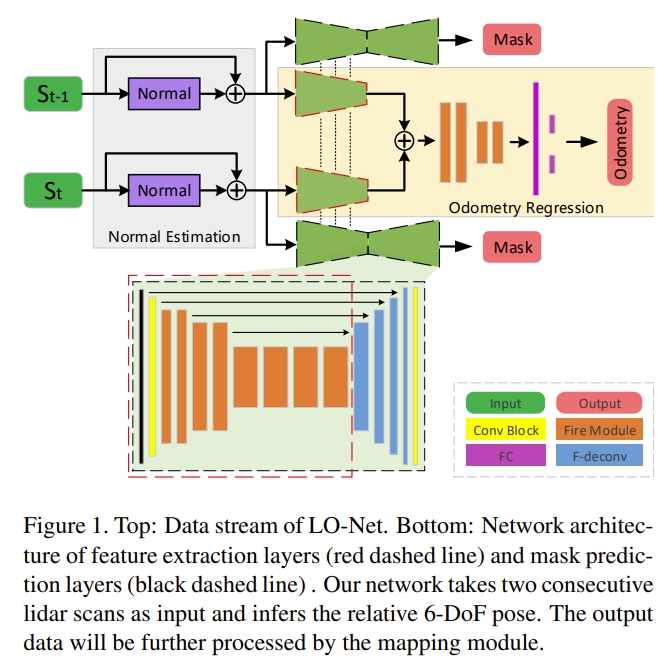
LONet: deep real-time LiDAR odometry
LONet是首个基于learning的lidar odometry,依赖于CNN的拟合能力。输入两个lidar scans,直接输出两者的relative motion。
网络end-to-end训练,没有任何的几何约束,容易出现overfitting的情况.
|
|
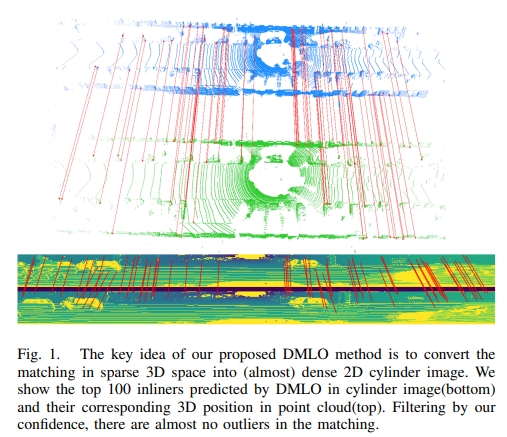
DMLO: Deep Matching LiDAR Odometry
DMLO在框架中明确强制执行几何约束,将6DoF姿态估计分为两个部分:
- learning-based matching network给两个lidar扫描提供精确的correspondence
- 通过近似的奇异值分解(SVD)来估算刚体变换。
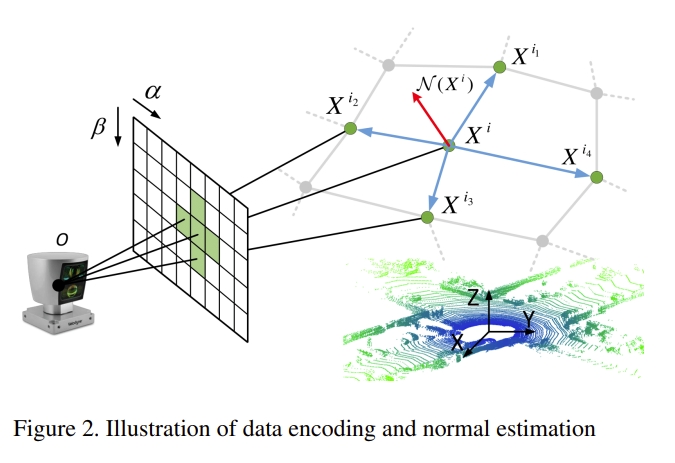
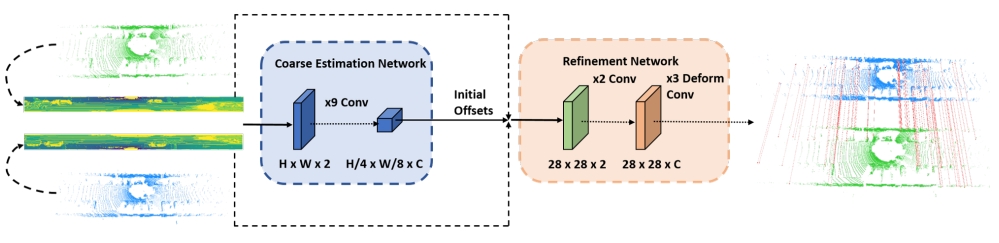
将所有的lidar信息编码成2D的图像(如下图所示),进而可以通过CNN来提取feature以及局部的相似性,进而计算出scans之间的数据关联。
而对于所获得的correspondence,也会额外估算其对应的权重,而对于获得的这些点云对( matched pairs)再通过SVD来计算姿态变换。直观来看,有点像基于learning的point cloud registration+SVD进而实现lidar-based odometry.
Self-supervised Learning of LiDAR Odometry for Robotic Applications
关键点:
- no labeled or ground-truth data is required
- applicable to a wide range of environments and sensor modalities without requiring any network or loss function adjustments
- 6-DOF pose, being able to operate in real-time on a mobile-CPU.
对于lidar的点云,一般有三种处理的方式:
- 将点云投影到2D image,然后用基于image的架构处理(比如Rangenet++)
- 使用基于voxel的3D卷积(比如Voxnet,high memory-requirement)
- 直接作用在disordered point cloud scans(比如Pointnet)
而本文采用的是第一种。
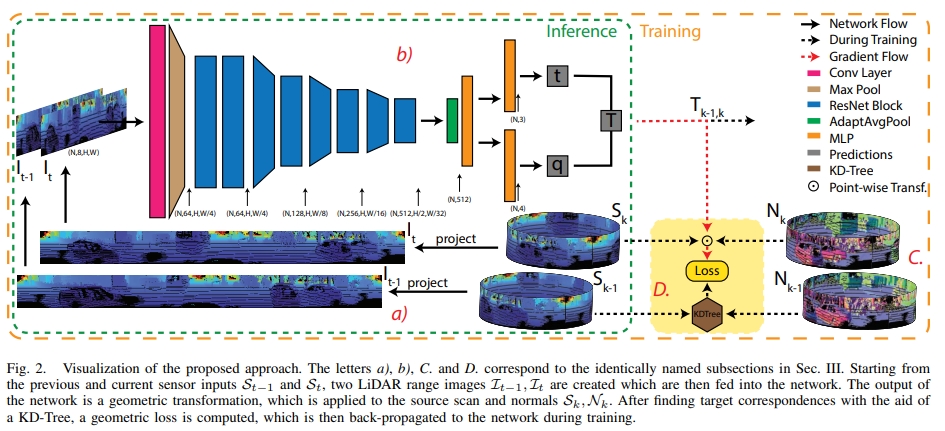
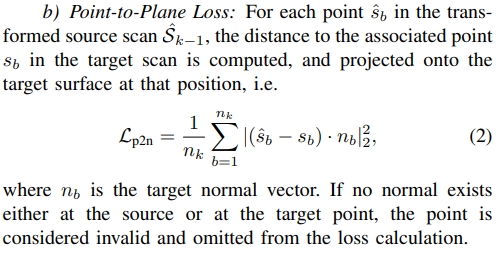
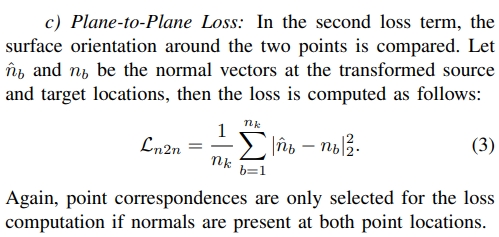
通过KD-Tree寻找到所有的点云的 source 和 target的对应,构建point-to-plane 和 plane-to-plane 的loss.
|
|
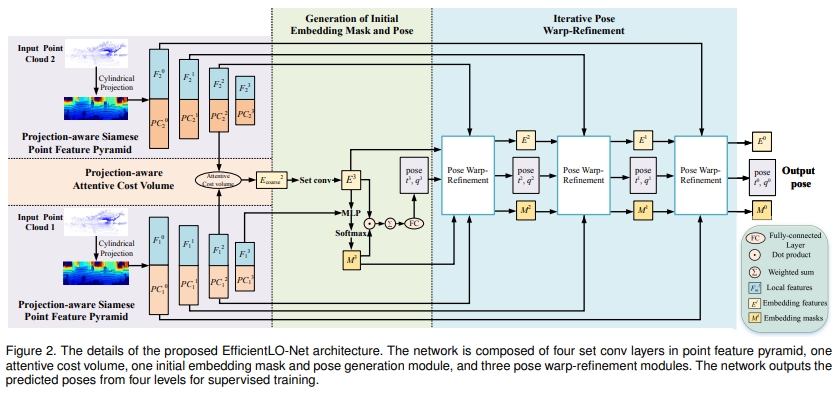
Efficient 3D Deep LiDAR Odometry
首先提出了一种projection-aware representation of the 3D point cloud,然后提出了一个Pyramid, Warping, and Cost volume (PWC) 架构,而关于点云之间的关联则是采用projection-aware attentive cost volume
针对点云表达、数据关联、(动态点云)、如何提取有效的信息这四个问题,分别提出对应的模块针对处理。
Translo: A window-based masked point transformer framework for large-scale lidar odometry
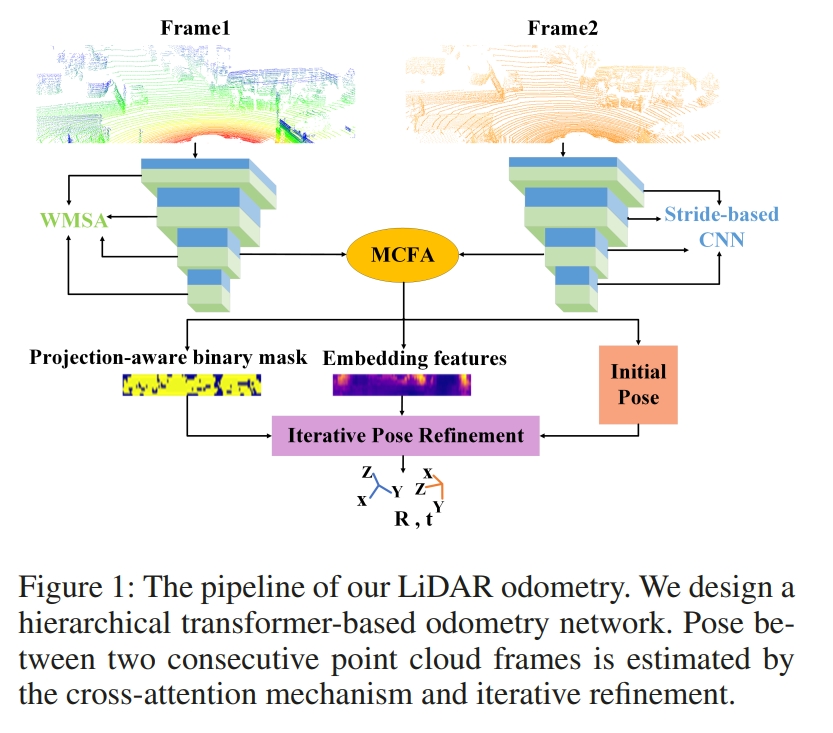
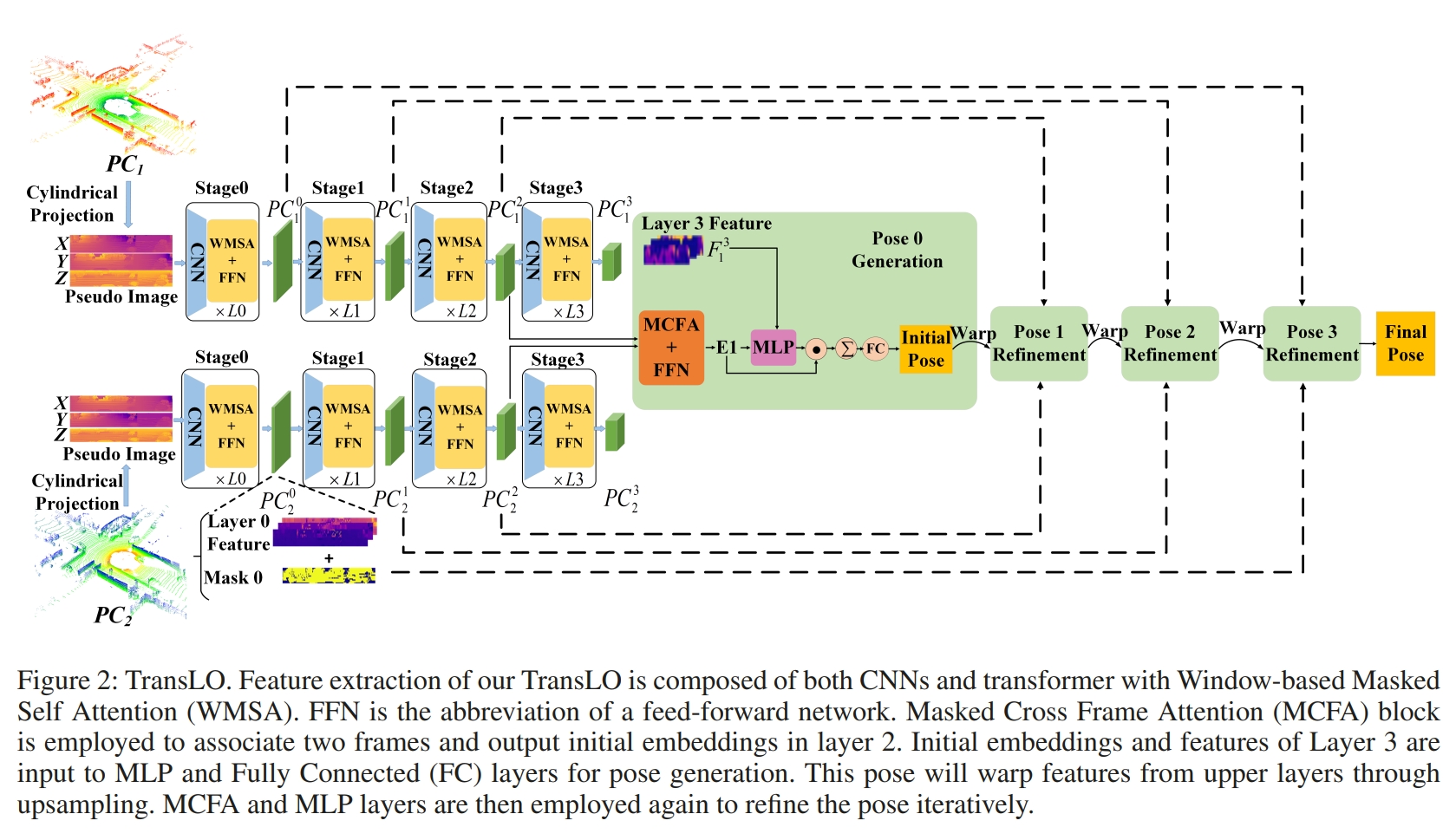
这个工作则是基于transformer的lidar odometry(the first transformer-based LiDAR odometry network)
而点云则是也是投影到2D 图像平面来处理的project point clouds onto a cylindrical surface to get pseudo images
|
|
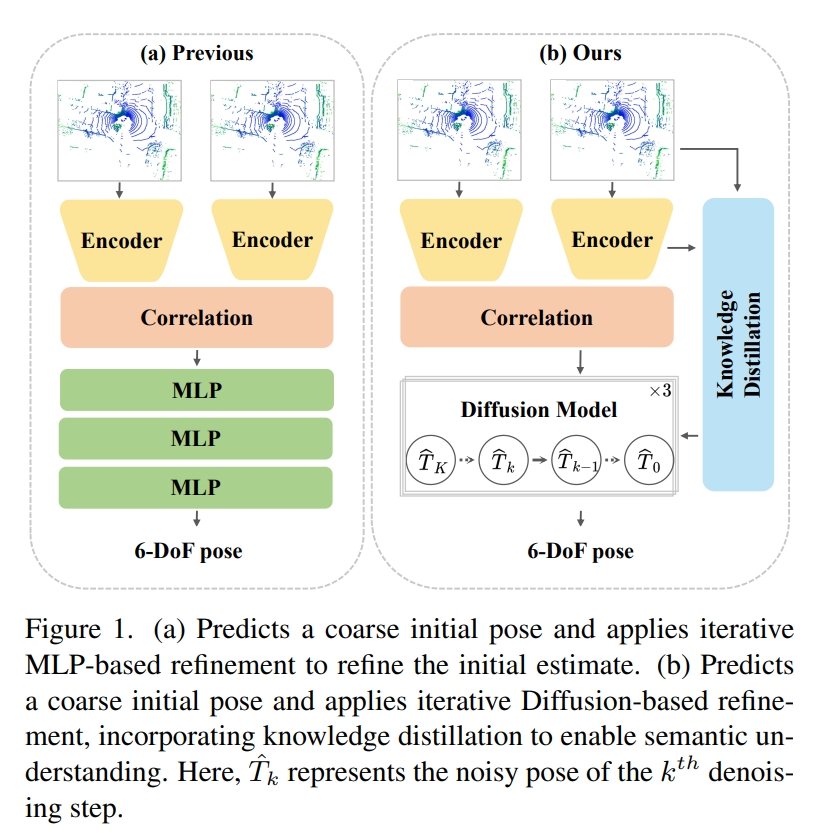
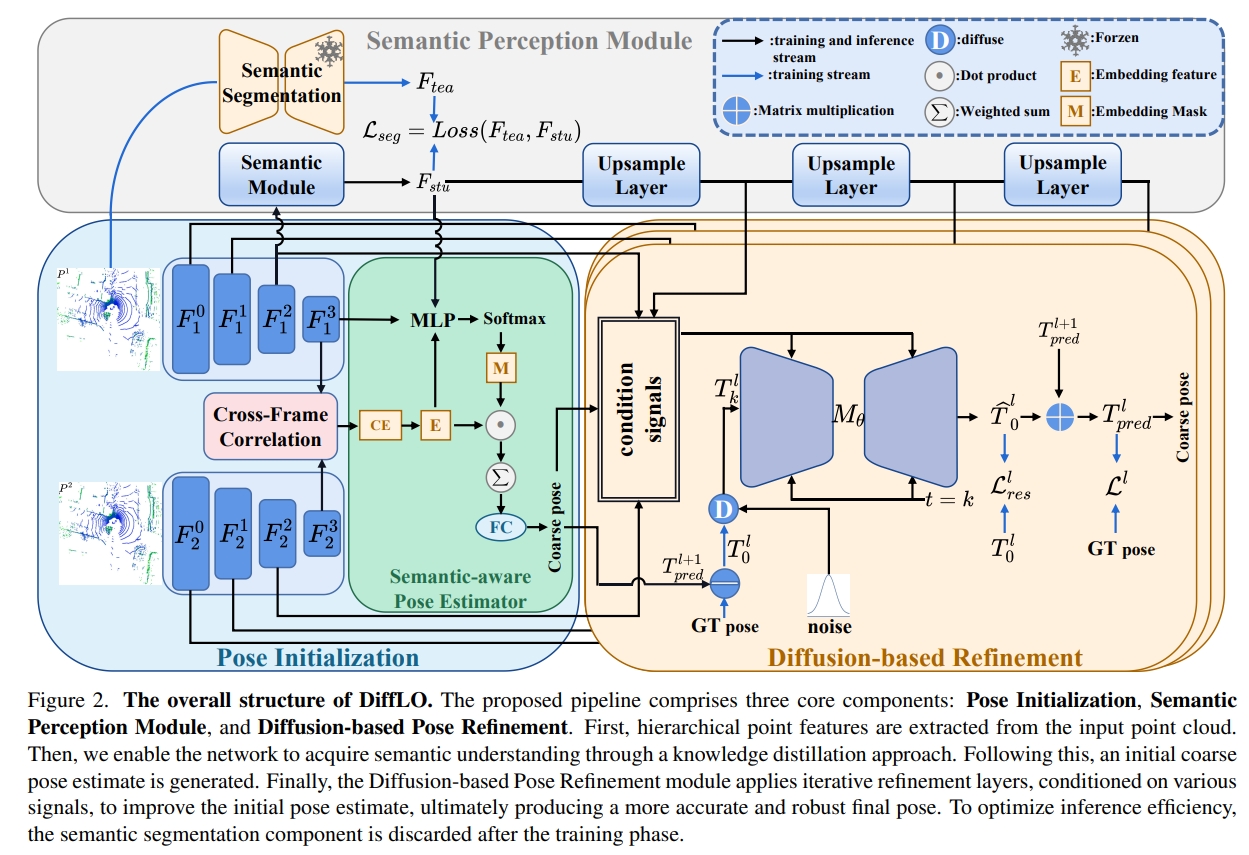
DiffLO: Semantic-Aware LiDAR Odometry with Diffusion-Based Refinement
直观理解为将MLP或者ICP对coarse initial pose refine的过程用Diffusion来做 (the first diffusion-based LiDAR odometry network)
|
|
点云的特征提取则是采用PointConv。而对于图中的语义感知模块,在推理的时候都需要retraining
Pointconv: Deep convolutional networks on 3d point clouds
PointConv将点云的位置(xyz)作为输入,用MLP来学习权重函数,并对学习到的权重采用inverse density scale来补偿非均匀采样。
可以看成是2D图像的卷积扩展到3D点云,采用MLP来实现density re-weighted convolution同时通过memory efficient的实现让其可以易于拓展。
treat convolution kernels as nonlinear functions of the local coordinates of 3D points comprised of weight and density functions.perform convolution on 3D point clouds with non-uniform samplingPointConv involves taking the positions of point clouds as input and learning an MLP to approximate a weight function, as well as applying a inverse density scale on the learned weights to compensate the non-uniform sampling.
对于一张2D图像,其可以展开为2D的离散网格阵列,对应的卷积可以看成如下表达:
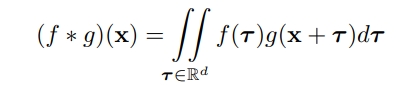
对于每个CNN的filter都是一个固定的小区域(比如3x3或者5x5等)
而对于点云数据,其是一系列3D点,每个点包含了xyz的位置向量以及对应的特征(比如颜色、表面法线等)。 相比起2D图像而言,点云的形状更加的灵活,其不在是在固定的网格中的点,而是可以是任意的连续值。因此传统的离散卷积将不可以直接用于点云上。而本文所提出的PointConv则是回归到3D卷积的连续版本上:
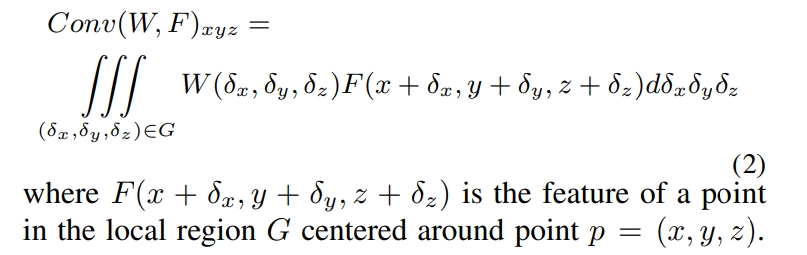
而点云可以看成是连续3D空间的非均匀采样:

而本文的关键点其实就是用MLP来实现上式中的权重函数W与3D坐标的关联。而对上式中的逆密度函数S则是通过a kernelized density estimation+MLP来近似。 进一步原理如下图3所示:
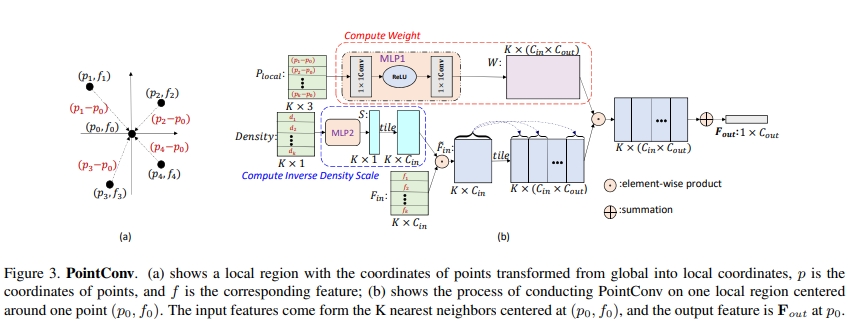
而PointConv中MLP的权重则是在多有的点云间share weight的。
DELO: Deep Evidential LiDAR Odometry using Partial Optimal Transpor
则是采用将点云降采样为固定的数量的点,然后用graph cnn来编码获取特征。然后也用transformer进行数据关联,然后再通过一个网络来估算变换以及用GTSAM来优化姿态:
|
|
PWCLO-Net: Deep LiDAR Odometry in 3D Point Clouds Using Hierarchical Embedding Mask Optimization
这个工作是直接作用在点云上的(处理原始点云的思路参考Pointnet++).通过计算两帧点云的a weighted soft correspondence
通过一个 internal trainable embedding mask来滤除遮挡点云或者动态点云。
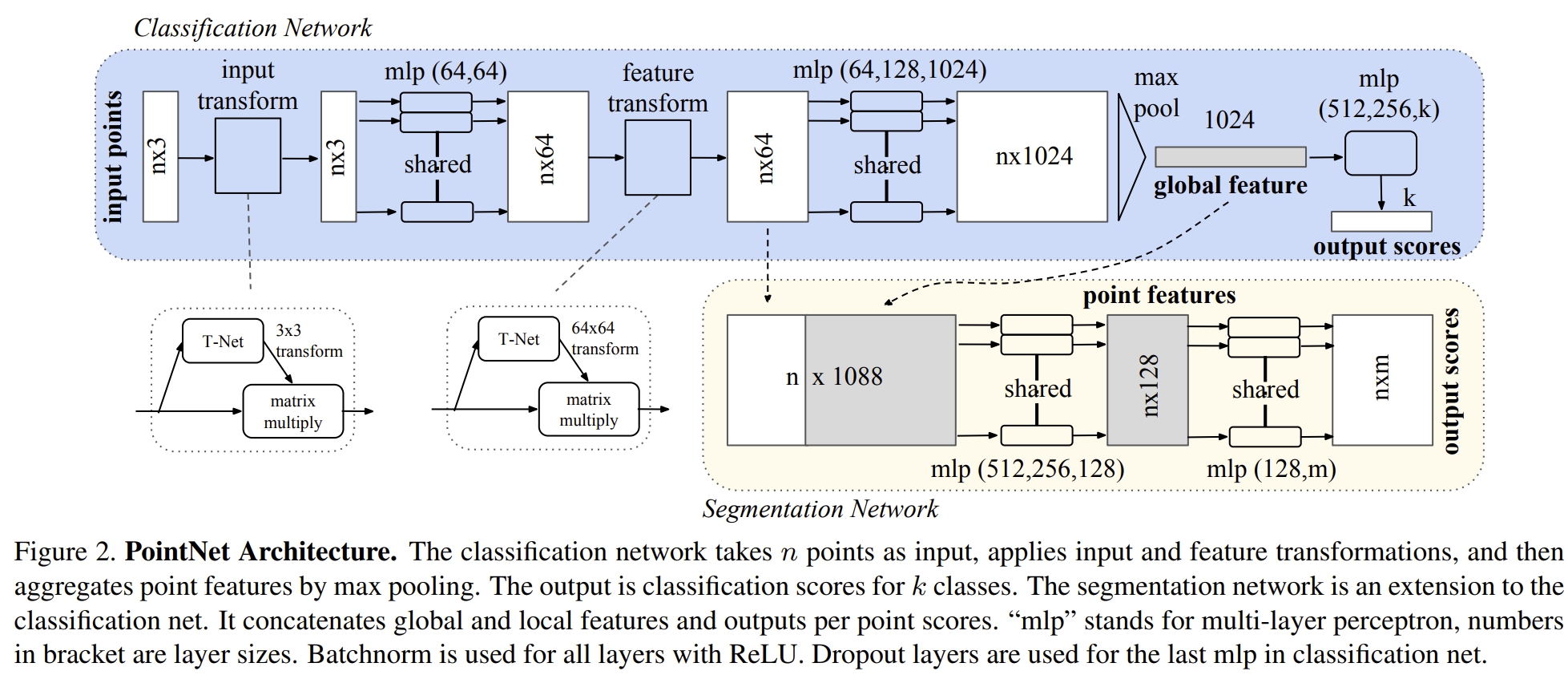
Pointnet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space
在PointNet的基础上加了一个hierarchical structure
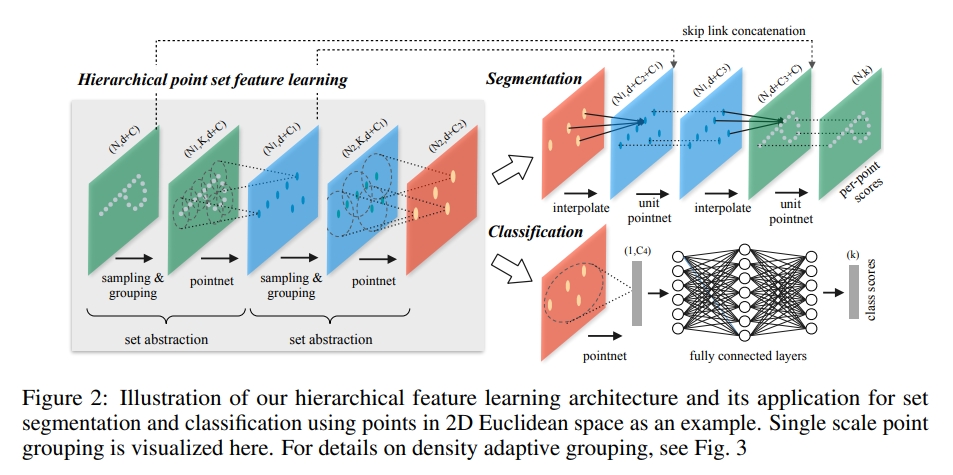
而PointNet的架构则是如下:
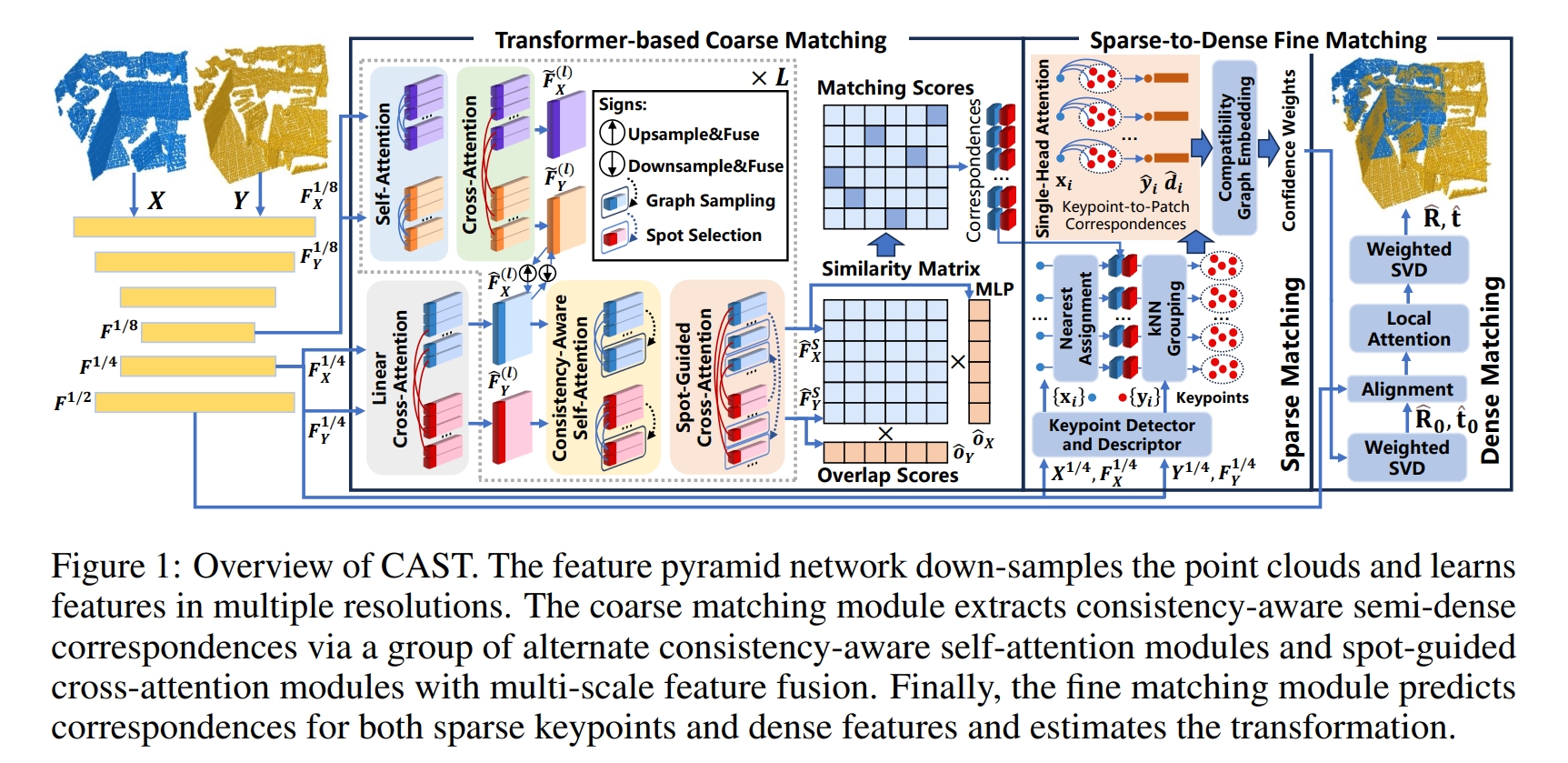
A Consistency-Aware Spot-Guided Transformer for Versatile and Hierarchical Point Cloud Registration
此处点云的预处理就是用的Kpconv,然后通过transformer以及coarse-to-fine matching network来计算两帧点云的相关性(如变换矩阵)
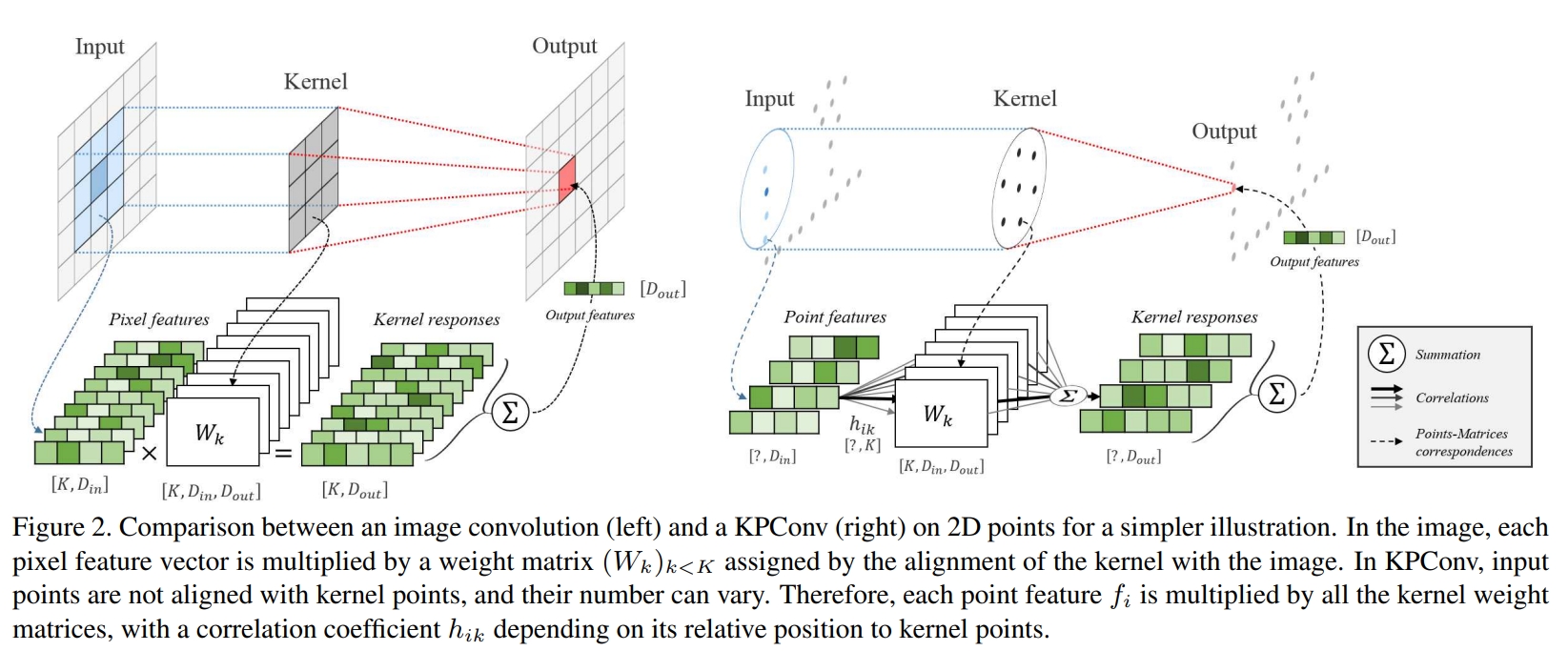
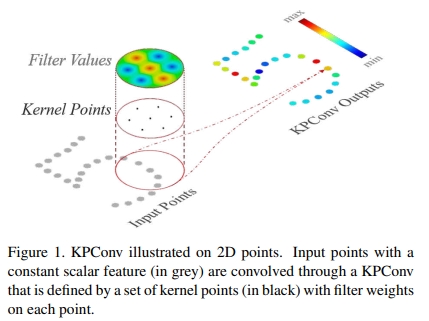
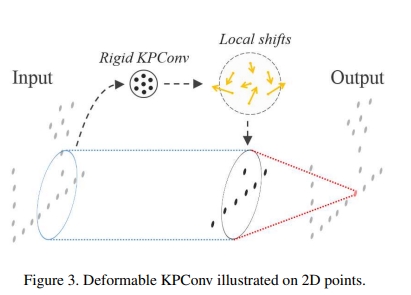
Kpconv: Flexible and deformable convolution for point clouds
收到image-based CNN的启发,对于一系列的kernel point定义一个kernel weight区域。如下图所示
|
|
相当于kernel weight是由点来携带的,类似于input features,而其影响的区域则是由一个相关的函数来定义。
下图是CNN与Kpconv的对比: