引言
本博文为本人针对基于人形机械狗等足式机器人的SLAM进行调研的记录
本博文仅供本人学习记录用~
- 引言
- Paper List
- Related Resource
- PPT Demonstration
- Paper Reading
- Humanoid locomotion and manipulation: Current progress and challenges in control, planning, and learning
- Advancements in humanoid robots: A comprehensive review and future prospects
- Comparative Evaluation of RGB-D SLAM Methods for Humanoid Robot Localization and Mapping
- A 3D Reconstruction and Relocalization Method for Humanoid Welding Robots
- Humanoid loco-manipulations using combined fast dense 3D tracking and SLAM with wide-angle depth-images
- Novel lightweight odometric learning method for humanoid robot localization
- Achievement of Localization System for Humanoid Robots with Virtual Horizontal Scan Relative to Improved Odometry Fusing Internal Sensors and Visual Information
- Leg-KILO: Robust Kinematic-Inertial-Lidar Odometry for Dynamic Legged Robots
- Online object searching by a humanoid robot in an unknown environment
- OptiState: State Estimation of Legged Robots using Gated Networks with Transformer-based Vision and Kalman Filtering
- Cerberus: Low-Drift Visual-Inertial-Leg Odometry For Agile Locomotion
- VILENS: Visual, Inertial, Lidar, and Leg Odometry for All-Terrain Legged Robots
- NaVILA: Legged Robot Vision-Language-Action Model for Navigation
- Contact-aided invariant extended Kalman filtering for robot state estimation
- Hybrid contact preintegration for visual-inertial-contact state estimation using factor graphs
- Online Kinematic Calibration for Legged Robots
Paper List
- 注意,此处非最新版,仅仅是写此博客的时候的记录
- Keep update the paper list in: Awesome-Humanoid-Robot-Localization-and-Mapping
Related Resource
- Survey for Learning-based VO,VIO,IO:Paper List and Blog
- Survey for Transformer-based SLAM:Paper List and Blog
- Survey for Diffusion-based SLAM:Paper List and Blog
- Survey for NeRF-based SLAM:Blog
- Survey for 3DGS-based SLAM: Blog
- Survey for Deep IMU-Bias Inference Blog
- Paper Survey for Degeneracy for LiDAR-based SLAM
- Reproduction and Learning of LOAM Series
- Awesome-LiDAR-Visual-SLAM
- Awesome-LiDAR-Camera-Calibration
- Overview of Humanoid Robots and 3D SLAM Works (in the PPT):
PPT Demonstration
Paper Reading
下面对细看的论文进行概述性解读
Humanoid locomotion and manipulation: Current progress and challenges in control, planning, and learning
首先建议看一下这篇人形机器人相关的综述。对人形机器人领域进行了系统性回顾。
Advancements in humanoid robots: A comprehensive review and future prospects
这也是一篇综述性论文,其中的Perception & Interaction一节对人形机器人相关的感知与交互做了介绍
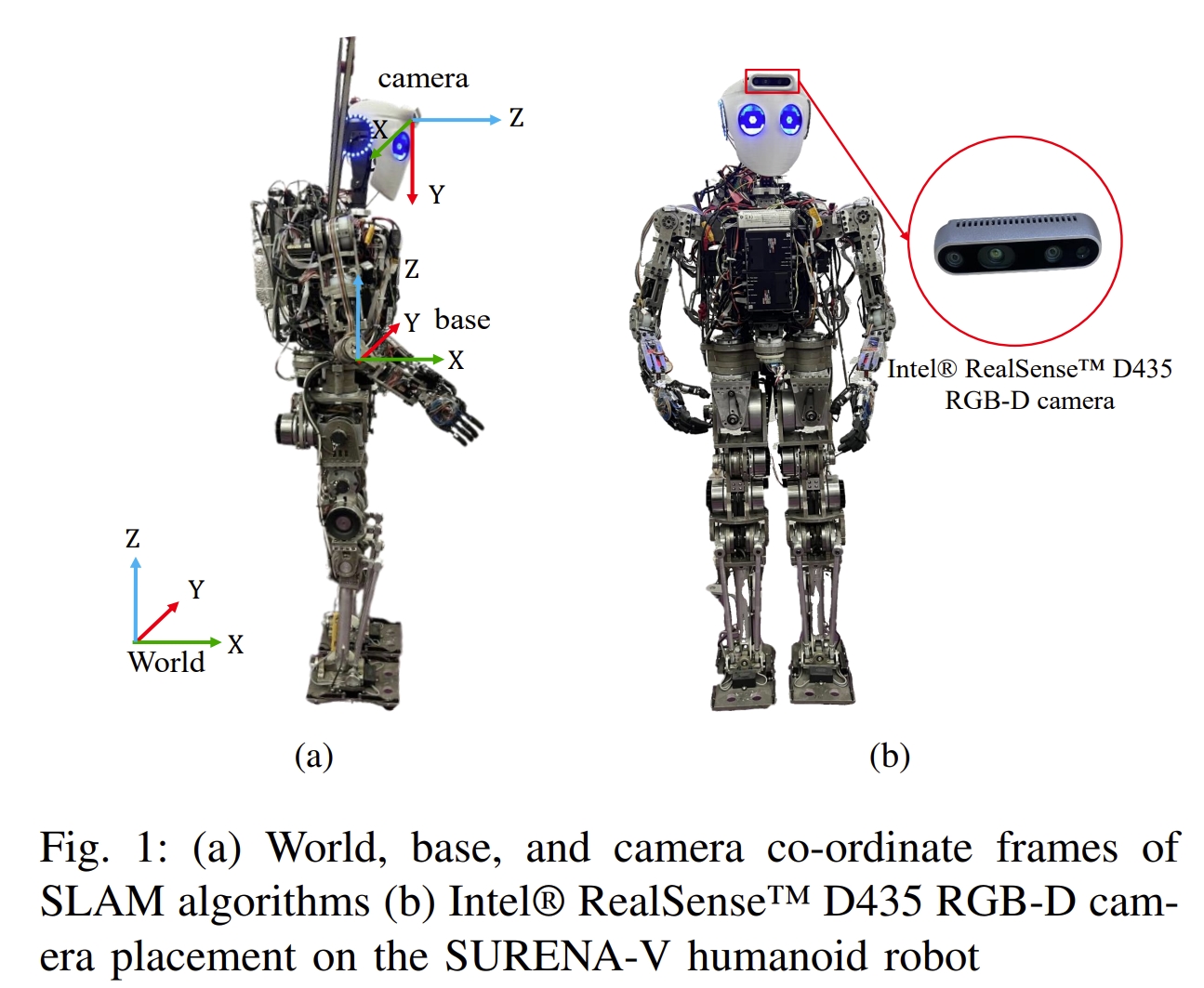
Comparative Evaluation of RGB-D SLAM Methods for Humanoid Robot Localization and Mapping
本研究通过对比评估了三种RGB-D SLAM算法在SURENA-V人形机器人的定位和地图构建任务中的性能。在定位精度方面,ORB-SLAM3表现最佳,其ATE为0.1073,次之为RTAB-Map(0.1641)和OpenVSLAM(0.1847)。然而,ORB-SLAM3和OpenVSLAM在机器人遇到具有有限特征点的墙壁时存在准确里程计的挑战。OpenVSLAM表现出在机器人接近初始位置时检测循环闭合并成功重新定位的能力。地图制作方面,RTAB-Map通过提供多样化的地图输出(密集地图、OctoMap和占据格地图)领先于ORB-SLAM3和OpenVSLAM,它们仅提供稀疏地图。
这篇论文只是普通的会议论文,只是把三种开源的方法(ORB-SLAM3, RTAB-MAP, OpenVSLAM)在人形平台上测试了一下,也没用结合人形机器人的特点来进行分析,单纯就是三个算法的分析,个人感觉参考价值不大~
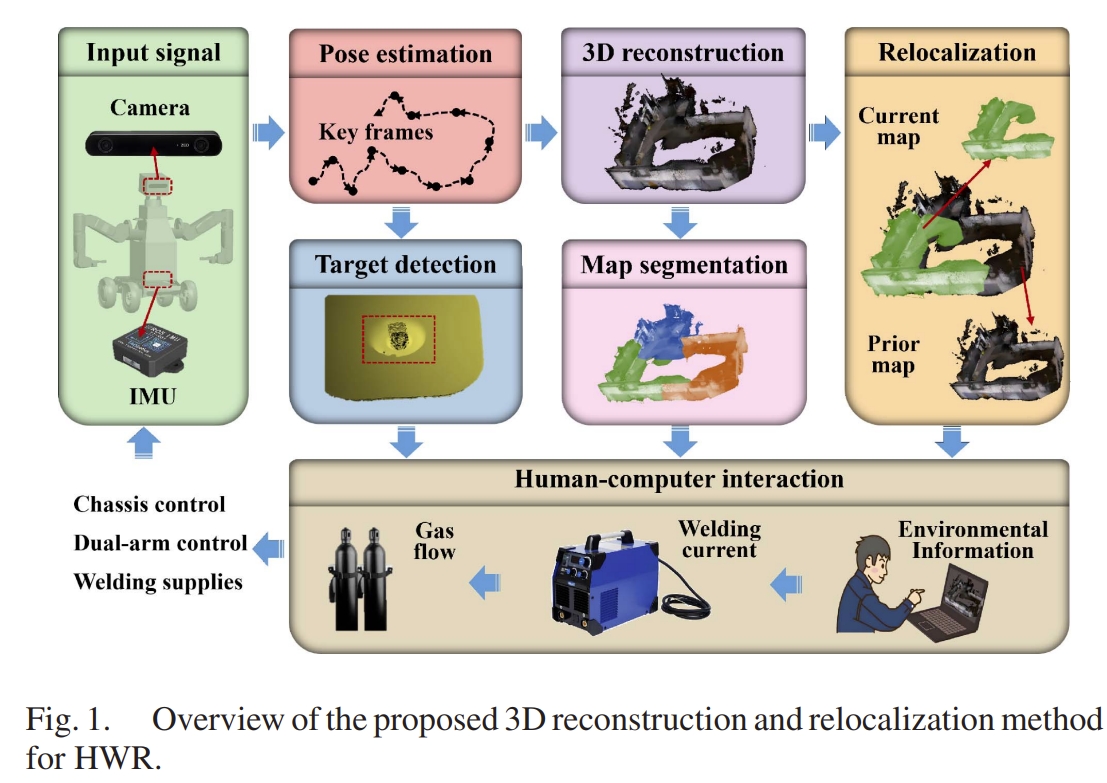
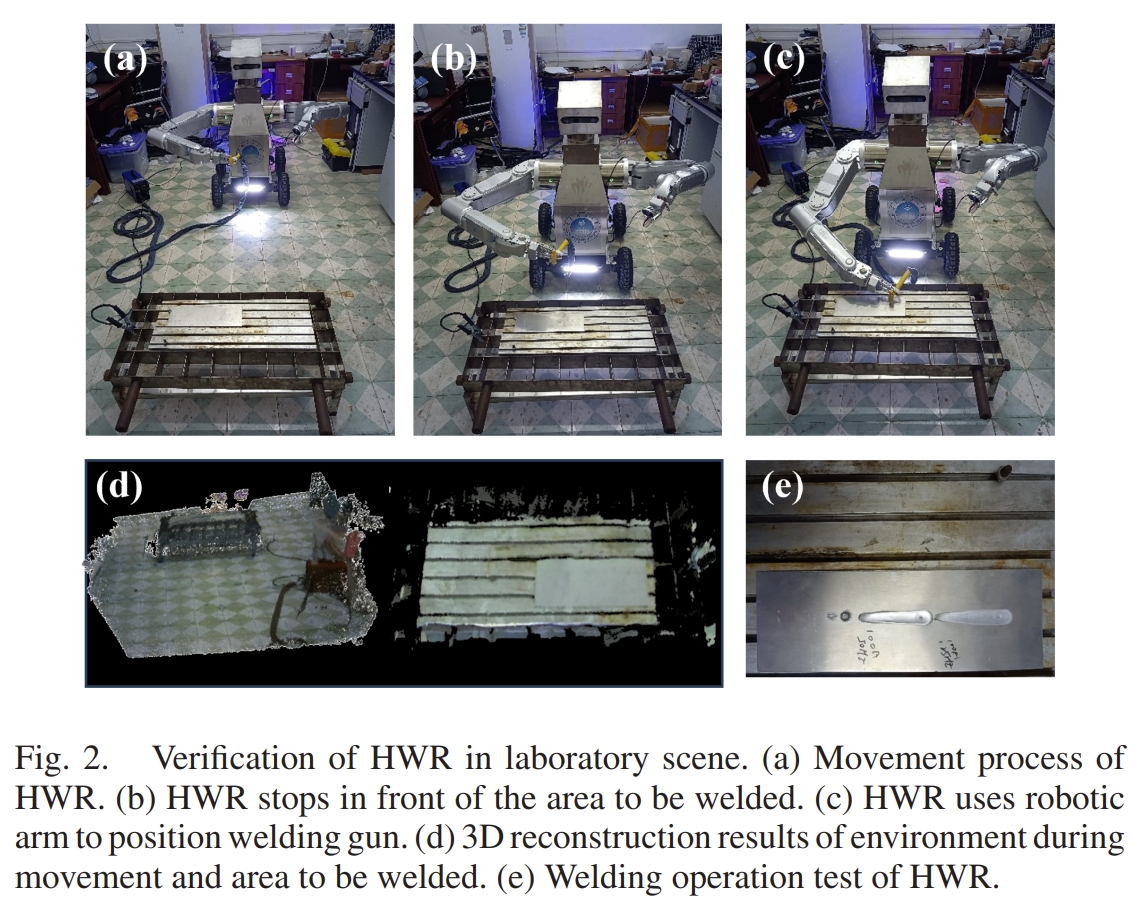
A 3D Reconstruction and Relocalization Method for Humanoid Welding Robots
本文的关键是给焊接机器人加上一个移动载体以及双臂,同时结合SLAM来进行姿态估计与三维重建。 其架构如下图所示。 通过RGB-D+IMU实现位姿的估计(应该是基于ORB-SLAM3开发的),同时结合深度相机可以获取三维环境信息。基于构建的3D地图,通过点云的匹配额外提供一个重定位的约束来进一步提升精度。 此外,对于3D地图会进行语义分割,并且结合YOLOv10来进行目标识别以此确认作业目标的位置。
|
|
Humanoid loco-manipulations using combined fast dense 3D tracking and SLAM with wide-angle depth-images
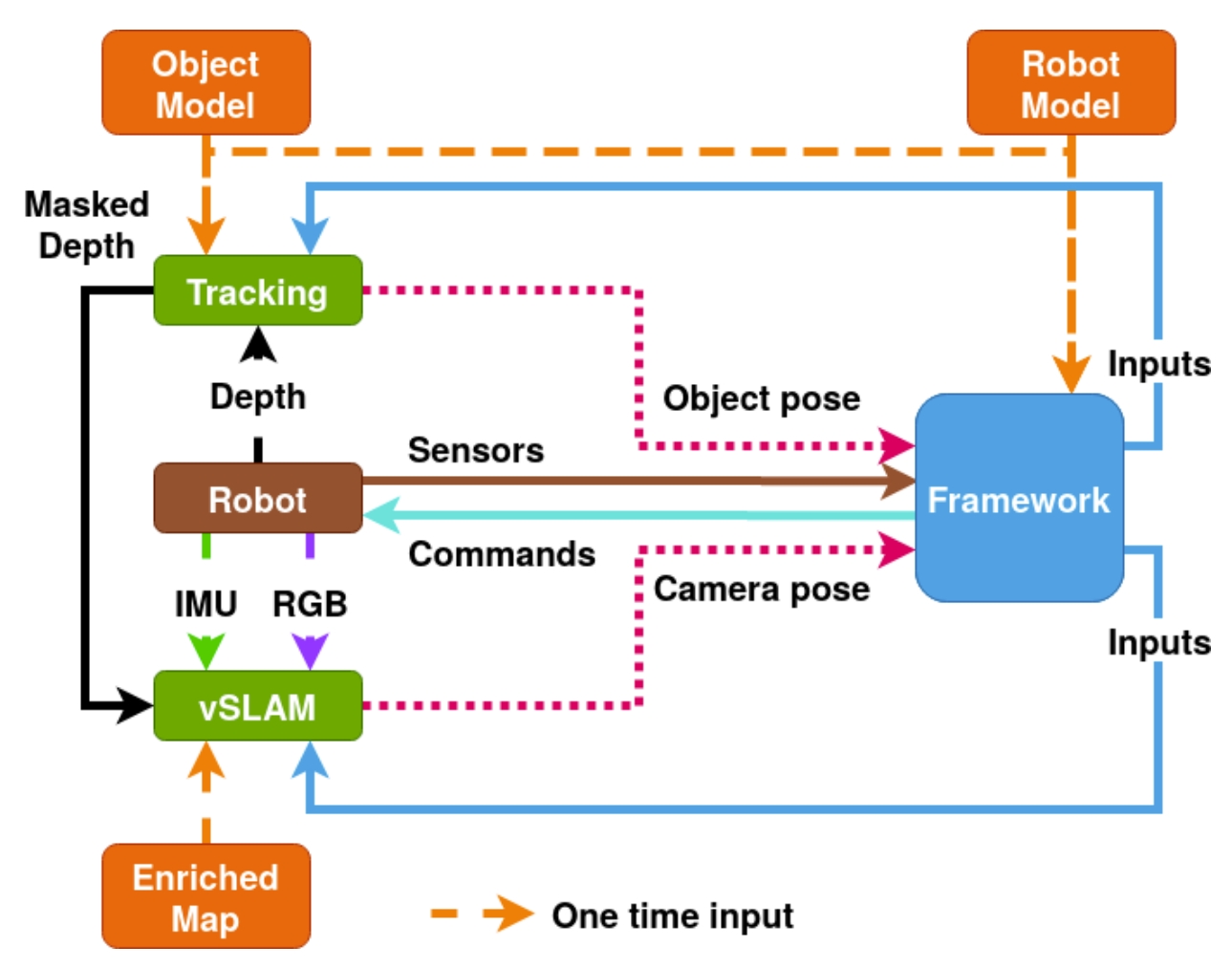
本文提出了一个结合基于视觉的跟踪定位作为人形机器人的whole-body 优化控制,看着似乎跟视觉伺服有点类似。 而为了将操作与定位更好的结合,作者提出了一个基于广角深度相机的稠密3D跟踪算法,并且跟SLAM结合起来。进而使得人形机器人可以实现在行走的同时来操作和组装大型的物体。
本文一个基本的insight就是,机器人手持着一个物体行走,那么这个物体对于机器人的视觉系统而言就是outlier,因此要去掉这个outlier,用其他的环境信息来进行定位。此外对于嵌入在人形机器人上的视觉系统而言,将四周的背景环境跟要操控的物体分割开来是非常重要的。

系统的框架如下图所示。所采用的SLAM算法是RTAB-Map,在其基础上添加对于机器人操作物体的跟踪
Novel lightweight odometric learning method for humanoid robot localization
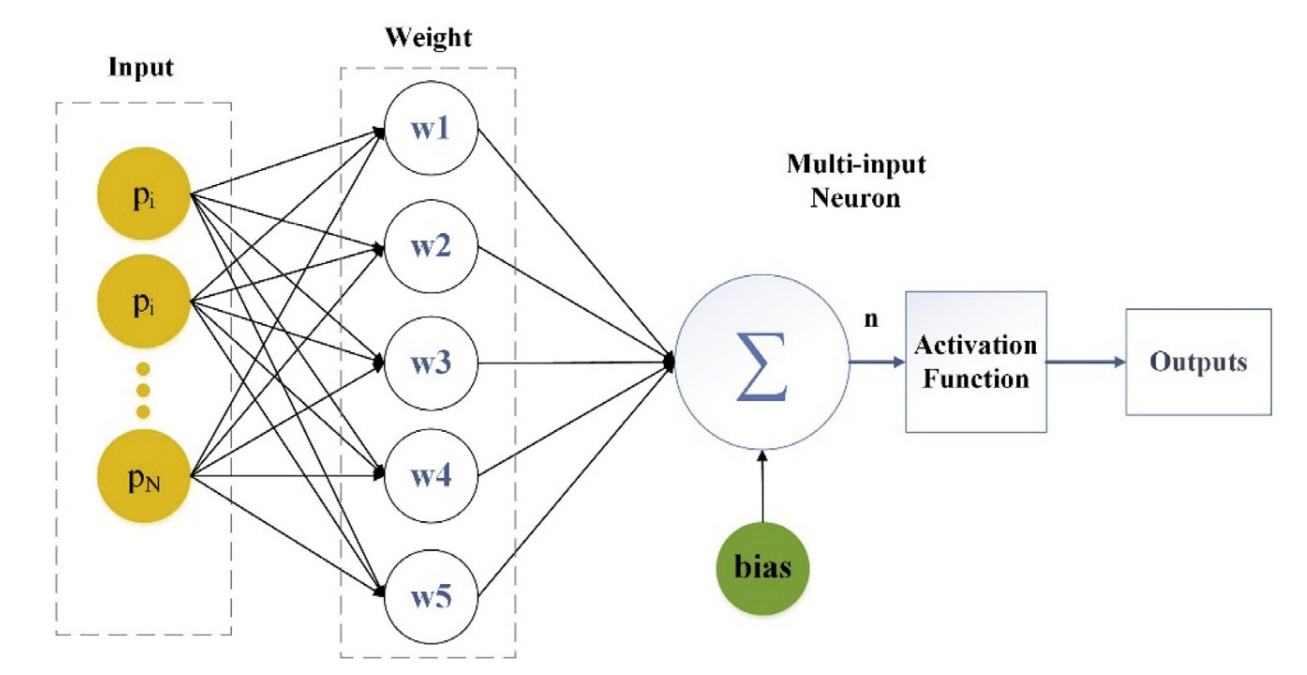
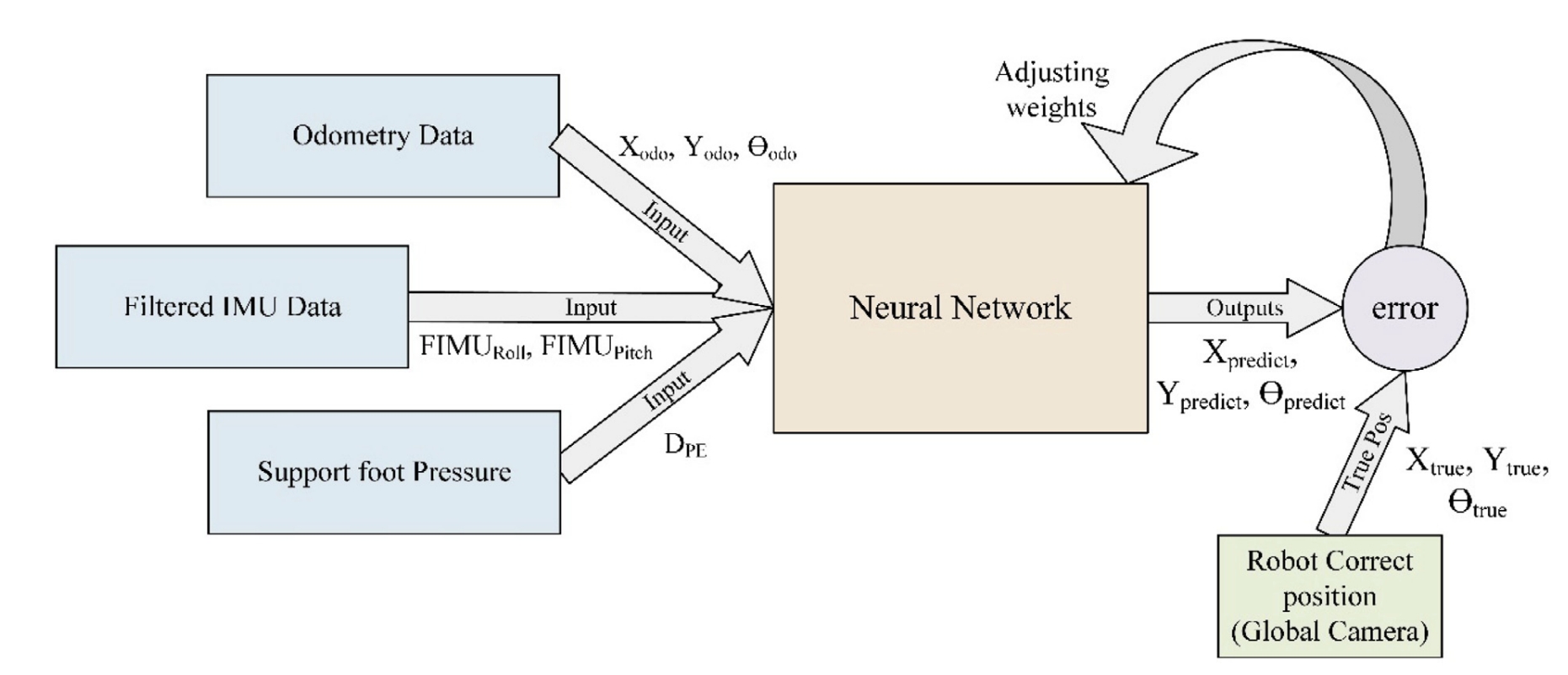
本文提出的就是基于人形机器人的惯性里程计(inertial odometry),不依赖于其他外部的感知,仅仅用IMU,并且采用ANN来进行运动学计算。 采用的网络是最基本的MLP,输入为来自人形机器人上的IMU、里程计、腿式压力等数据,输出直接为全局坐标系下的位置信息。如下图所示:
|
|
从实验的结果来看,所提提出的算法确实要比纯航位推算的精度要高(更加接近真值),但是运动的剧烈并不长,图上的单位是cm
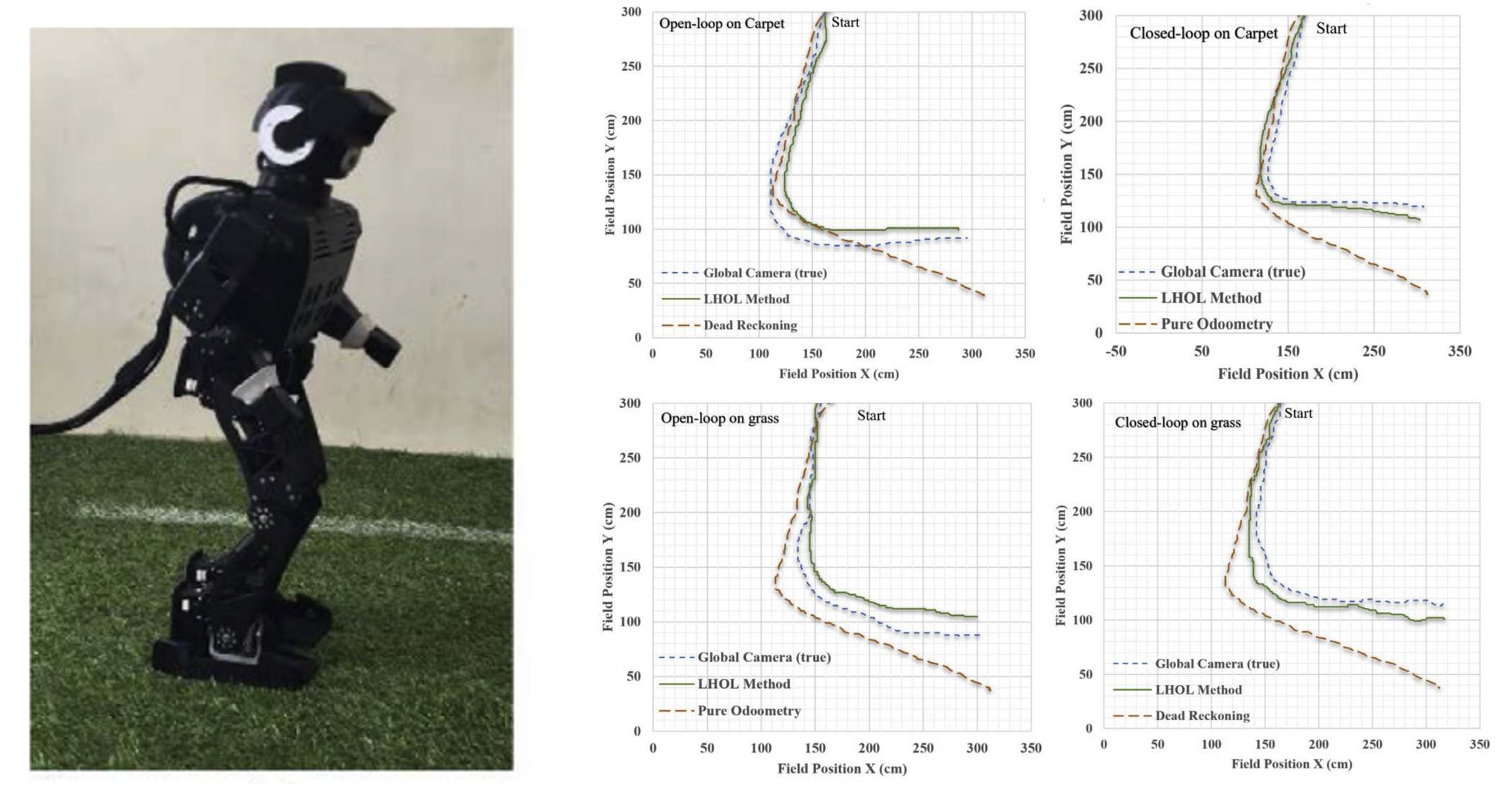
Achievement of Localization System for Humanoid Robots with Virtual Horizontal Scan Relative to Improved Odometry Fusing Internal Sensors and Visual Information
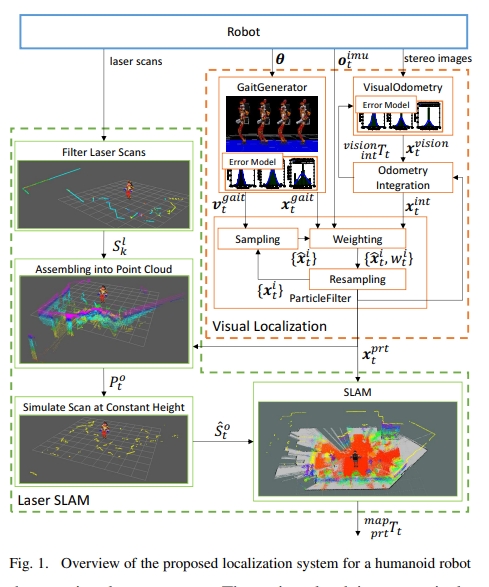
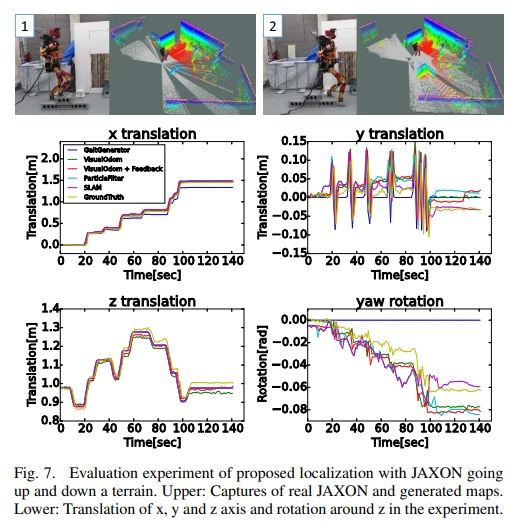
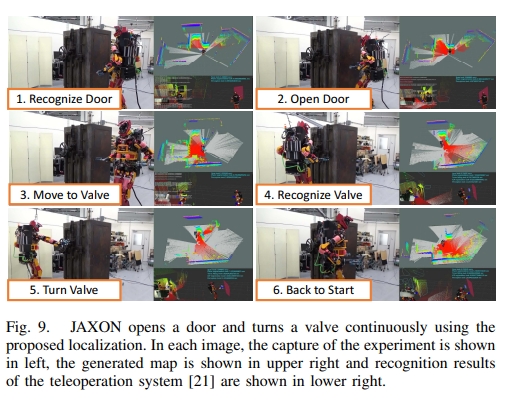
将视觉里程计、步态发生器的前馈命令以及惯性传感器的方位信息来提升里程计的性能。 进一步地,将该里程计用于从连续激光扫描的累积中生成3D点云, 然后对所获得的3D点云进行适当的切片,以创建高度固定的水平虚拟激光扫描。 而这个虚拟的激光扫描又进一步放到2D SLAM方法(也就是Gmapping)中来实现更高精度的SLAM。 其架构如下图所示:
|
|
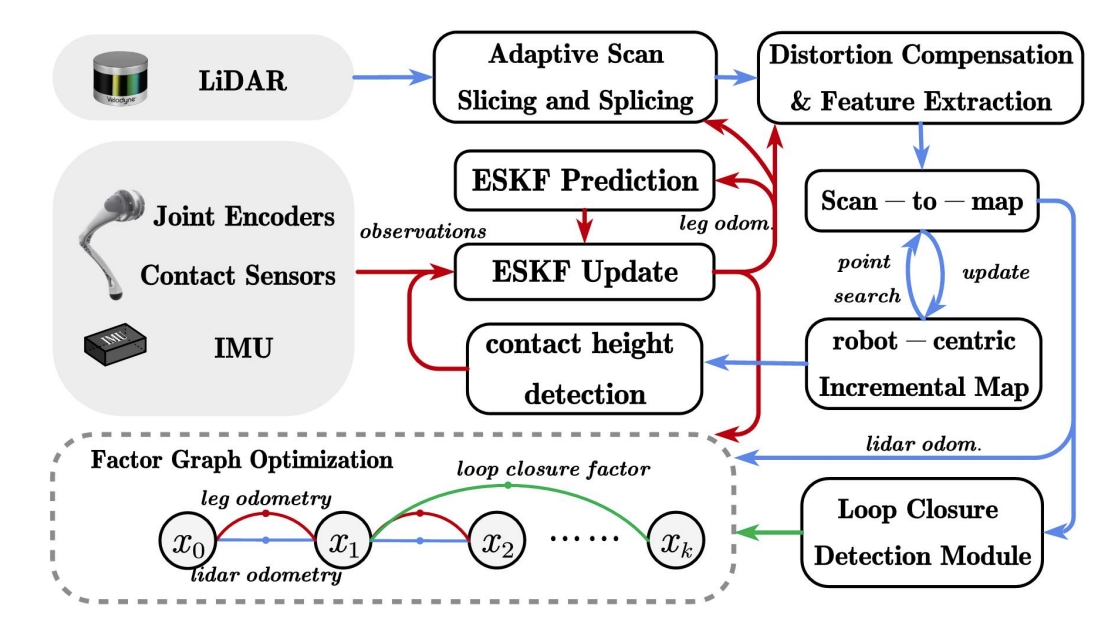
Leg-KILO: Robust Kinematic-Inertial-Lidar Odometry for Dynamic Legged Robots
本文提出基于四足机器人运动学的LIO。 足式机器人上高频的运动(如小跑步态)会引入频繁的脚部撞击,进而导致IMU的退化以及lidar的运动失真。 而直接用IMU观测的数据会容易导致明显的漂移(特别是在Z轴上)。 那么针对这些局限性,本文提出了基于图优化的腿式里程计、雷达里程计以及回环检测三者紧耦合的系统。
- leg odometry:提出了基于on-manifold error-state Kalman filter的运动惯性里程计,通过结合接触高度检测的约束来进一步减少高度方向的波动;
- lidar odometry:设计了一种自适应激光束切片和拼接的方法,以减轻高动态运动的影响;
- loop closure:提出机器人位中心的增量式建图方式来提高地图的维护效率;
系统的框架如下图所示
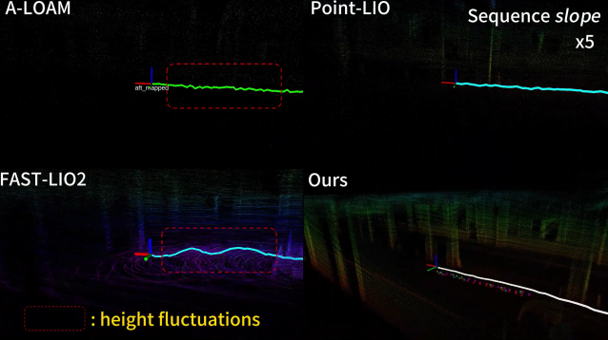
作者跟A-LOAM、Fast-LIO2以及Point-LIO进行了对比,值得一提的是,本文是基于LIO-SAM开发的,而LIO-SAM之前的测试经验是远不如Fast-LIO2以及Point-LIO的,但是在作者改动的框架下却可以超越这两者,可以看出所提出算法应该是有效的~
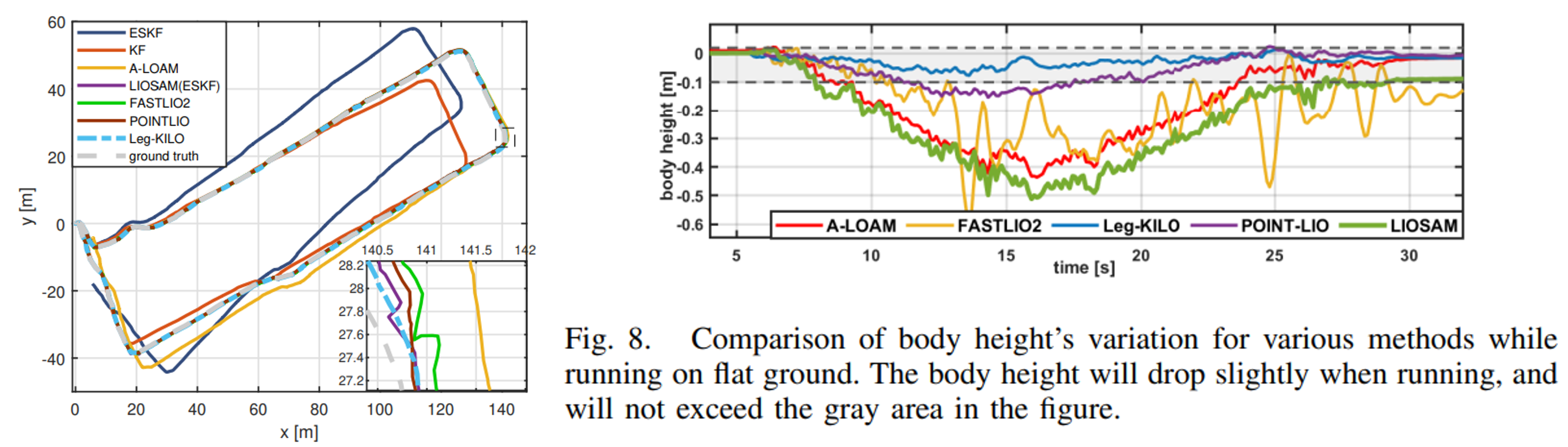
而在下右图的实验中也发现,在平地运动时,baseline方法均有较大的高度变化,而Leg-KILO则是在10cm以内。
Online object searching by a humanoid robot in an unknown environment
本文是通过结合3D SLAM来实现人形机器人在未知环境中寻找目标物体。 传统的方法都是需要一个静态的地图,同时需要有关于对象位置、区域大小限制或每次观察的离线视点规划时间等提示信息。而本文则是单纯基于目标物体的3D模型,在未知环境中寻找这个物体。 其框架如下图所示。 SLAM用的是RTAB-Map(但是生成的是2D map),同时结合机器人的运动规划(包括目标物体的3D点云,路径规划、避障以及自主探索)来实现整个系统。
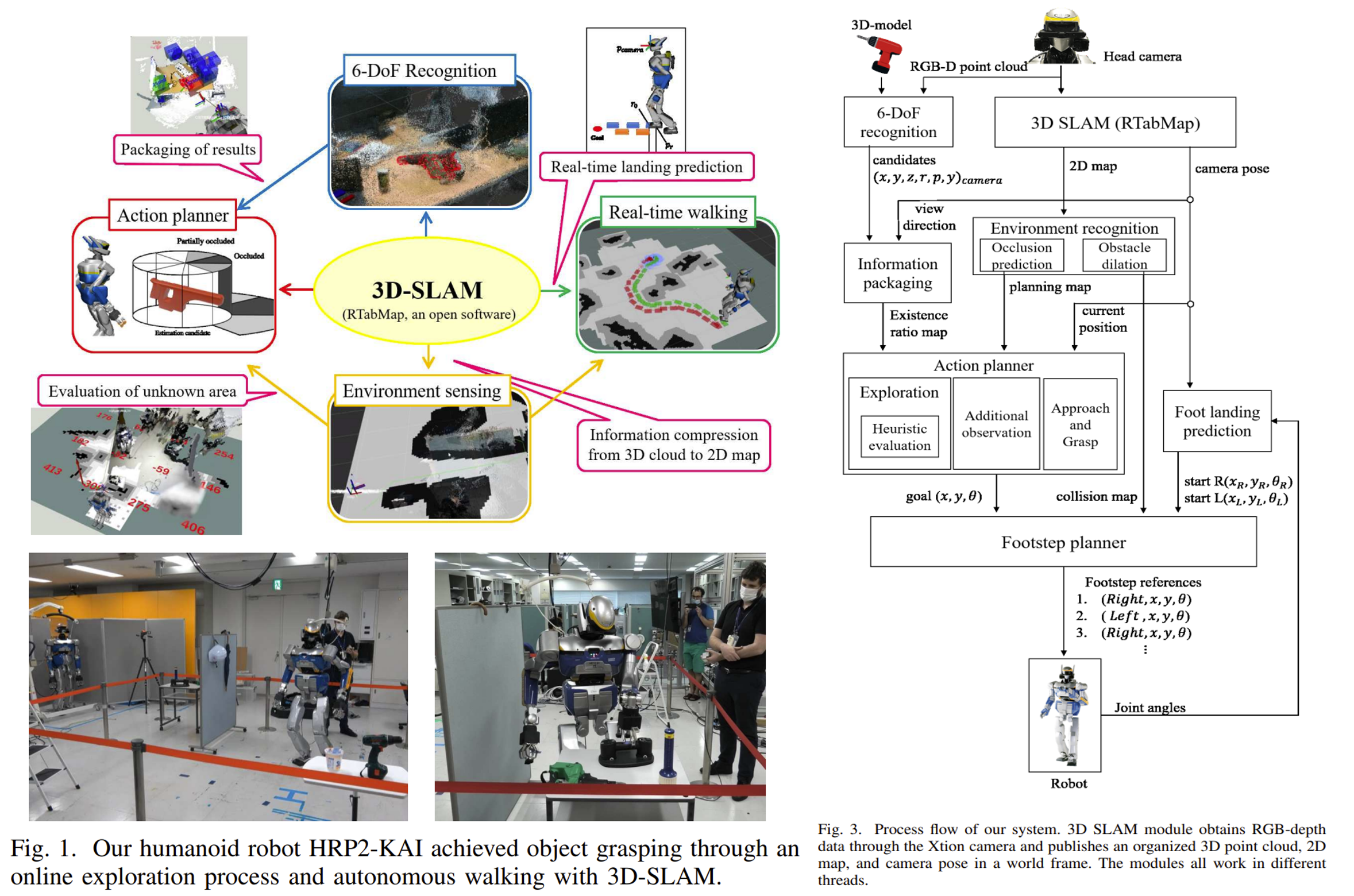
要完成一项任务需要四个主要部分:目标识别(object recognition), 环境感知(environment recognition), 运动规划 (action planning), 以及双足行走bipedal walking。
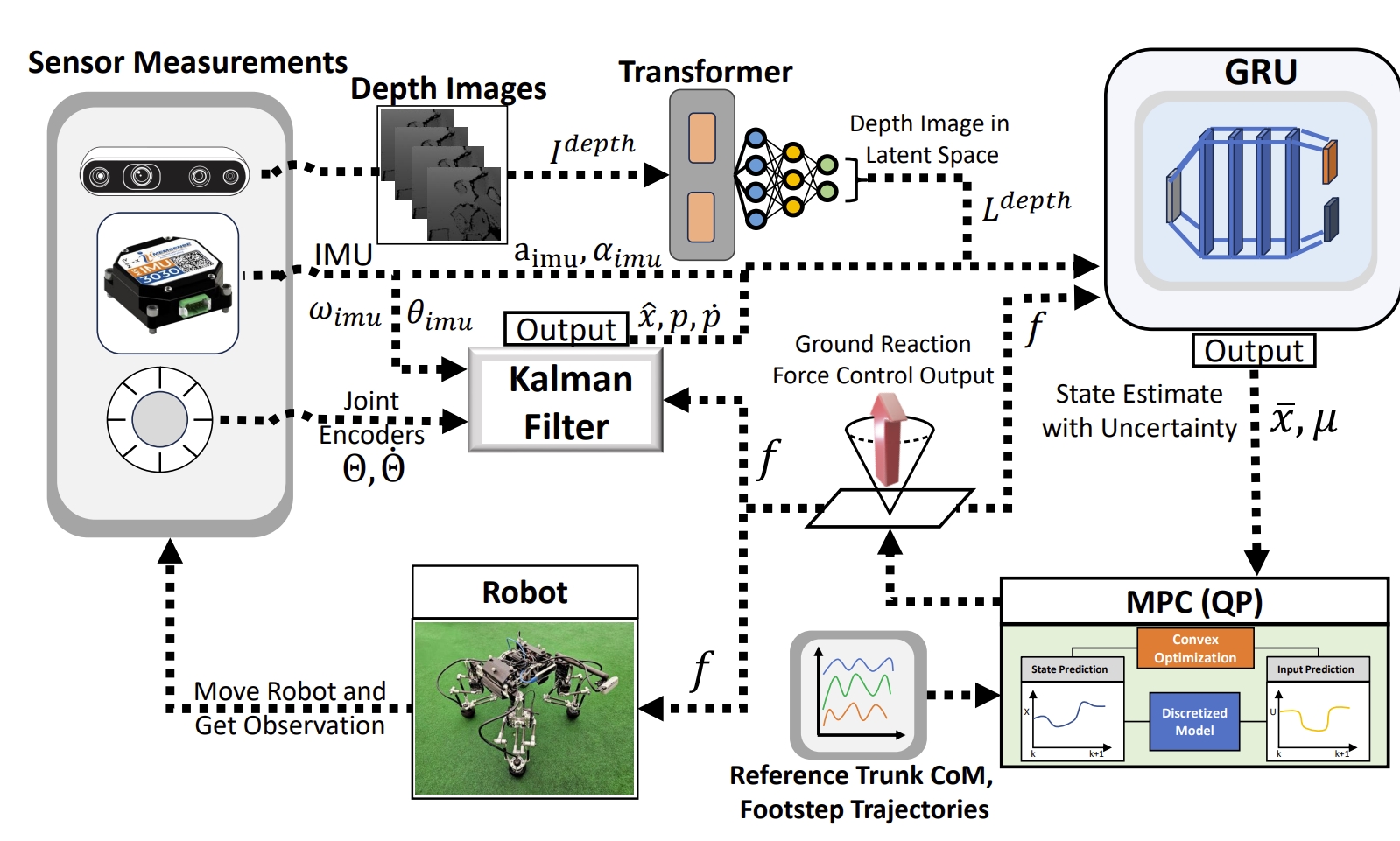
OptiState: State Estimation of Legged Robots using Gated Networks with Transformer-based Vision and Kalman Filtering
对于足式机器人而言,踏步容易引起相机的运动模糊,使得视觉数据不可靠。而由于机械腿与地面的不断接触和断开(还存在滑动),基于IMU等运动学信息也容易出错,特别是在有大干扰(比如障碍物)或柔性表面的情况。
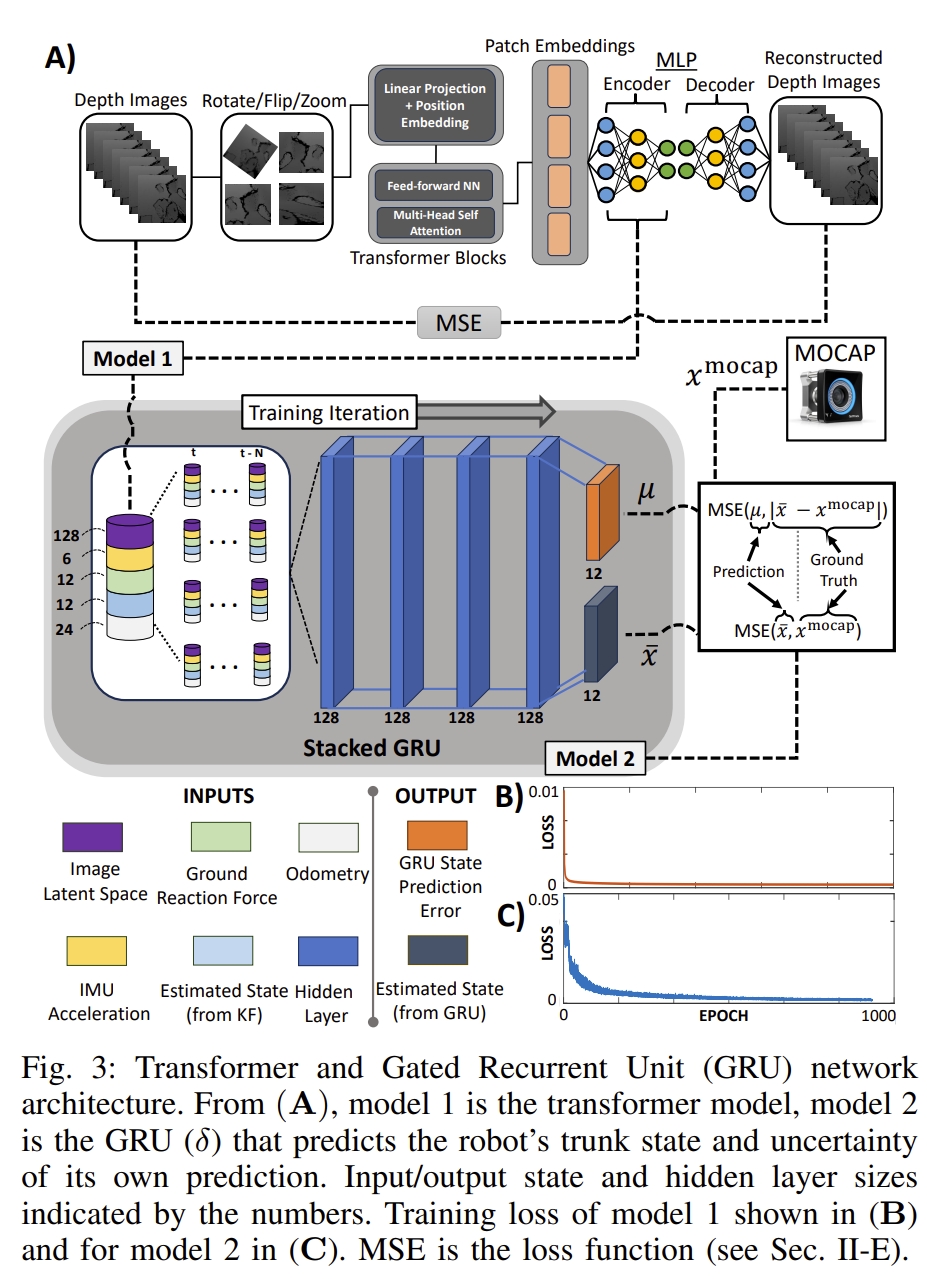
此外,由于腿式机器人产生的动态运动需要高频控制,因此低计算消耗、高精度的状态估计系统的也是必须的。 因此,该工作通过融合卡尔曼滤波、优化以及深度学习方法,提出了一个融合内部与外部传感器信息的机器人躯干状态估计算法。 首先采用卡尔曼滤波来对关节编码器以及IMU测量量进行状态预测,通过复用来自凸模型预测优化方法输出的地面反作用力来进行状态的更新。 而卡尔曼滤波的输出会输入GRU网络。
此外,GRU网络还会有来自Vision Transformer处理的深度图的latent feature(隐特征),而GRU输出的姿态信息将会与动捕提供的真值数据求loss来实现网络的训练。
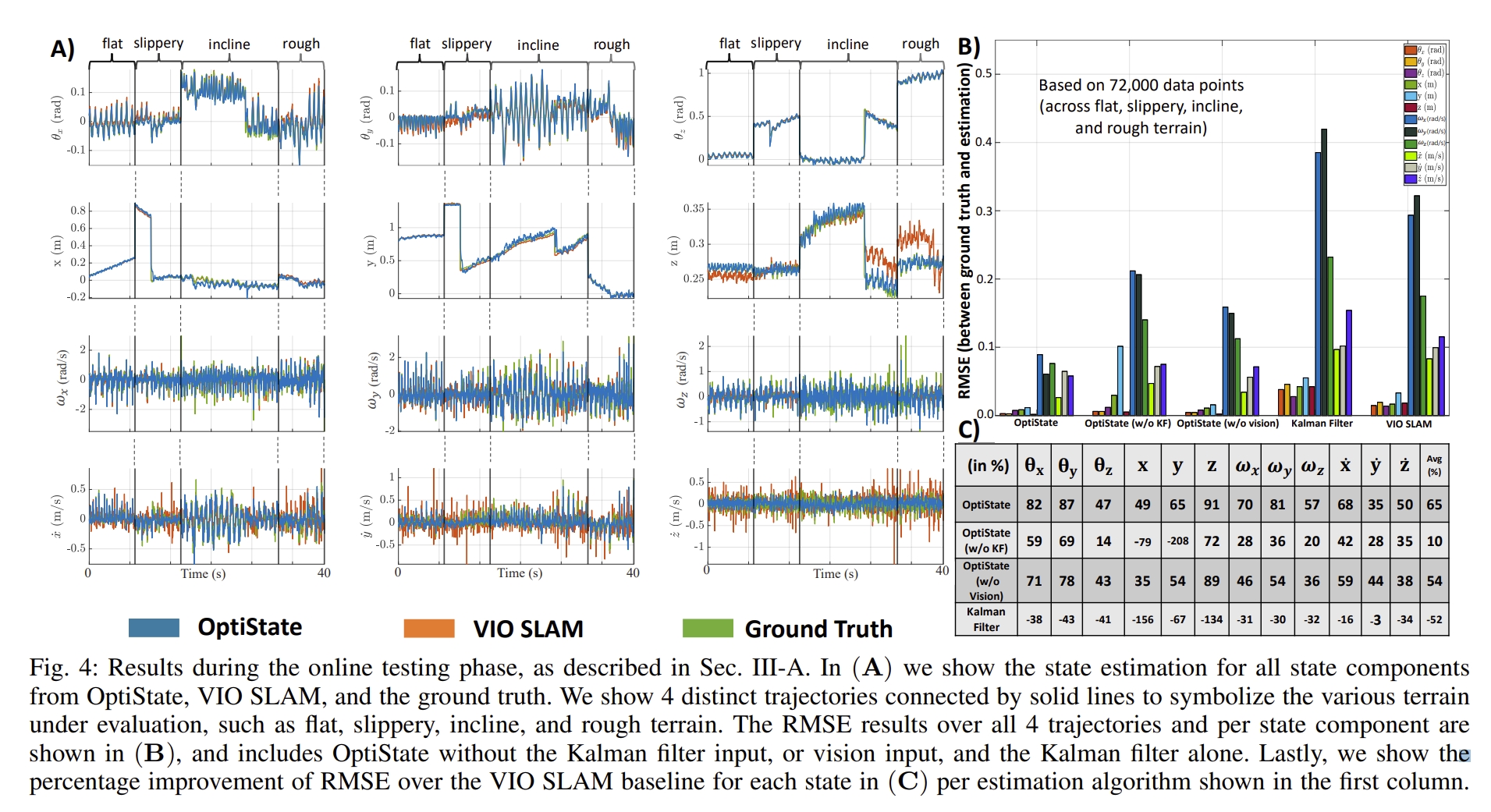
从结果来看确实OptiState的误差要比滤波以及VIO SLAM(来自RealSense T265 camera传感器的输出)要小
Cerberus: Low-Drift Visual-Inertial-Leg Odometry For Agile Locomotion
该工作提出了一个视觉-惯性-腿式里程计(Visual-Inertial-Leg Odometry, VILO), 包含的传感器有:双目图像、IMU、关节编码器、腿部接触传感器。 实现了在线的运动学参数的校正以及接触传感器的异常值剔除,进而减少了定位的漂移。 通过室内与室外的实验(450米远、平均运动速度0.5m/s室内,1m/s室外)也证明了所采用的运动学参数估算可以将累积误差减少的1%以内。
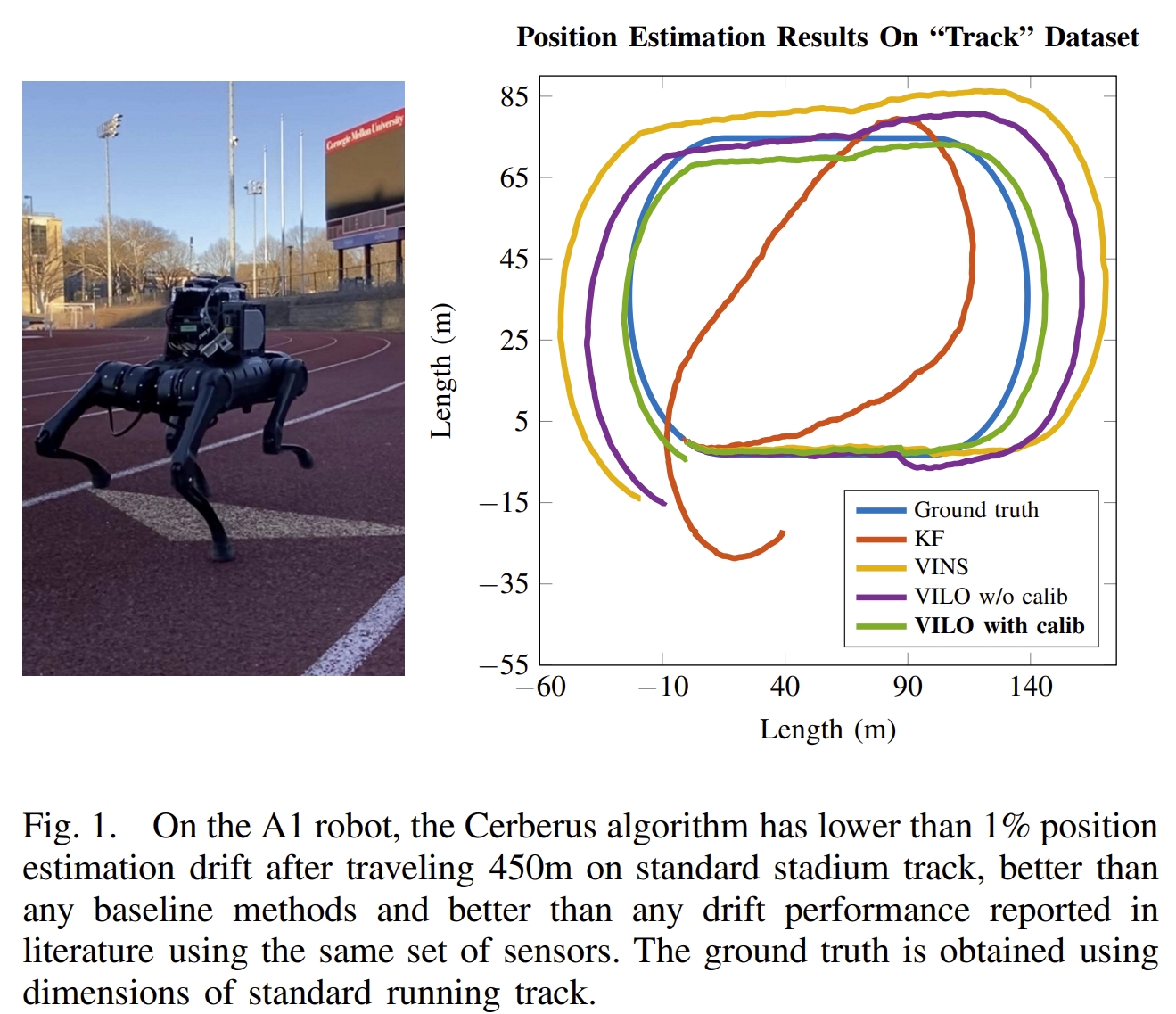
|
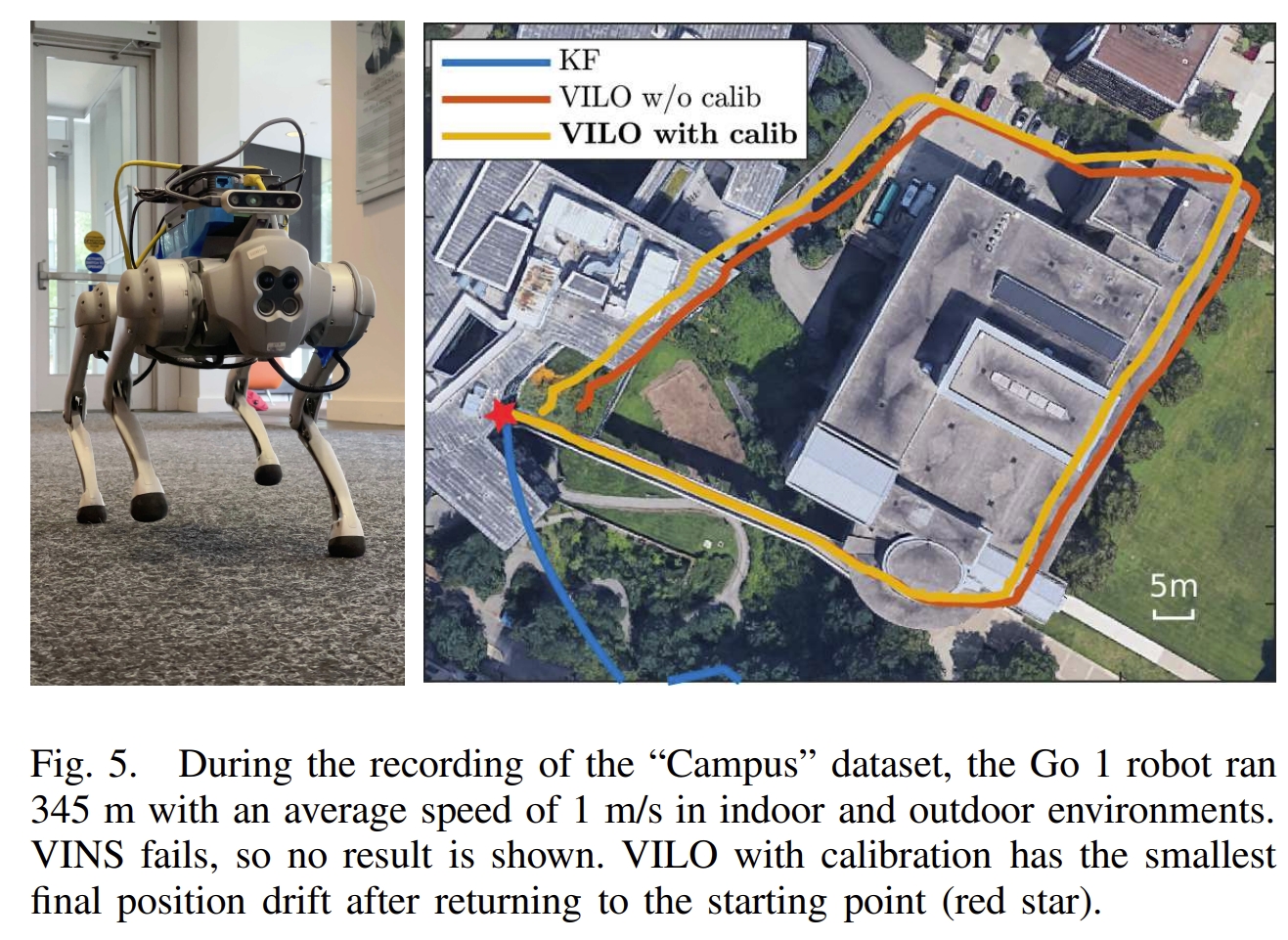
|
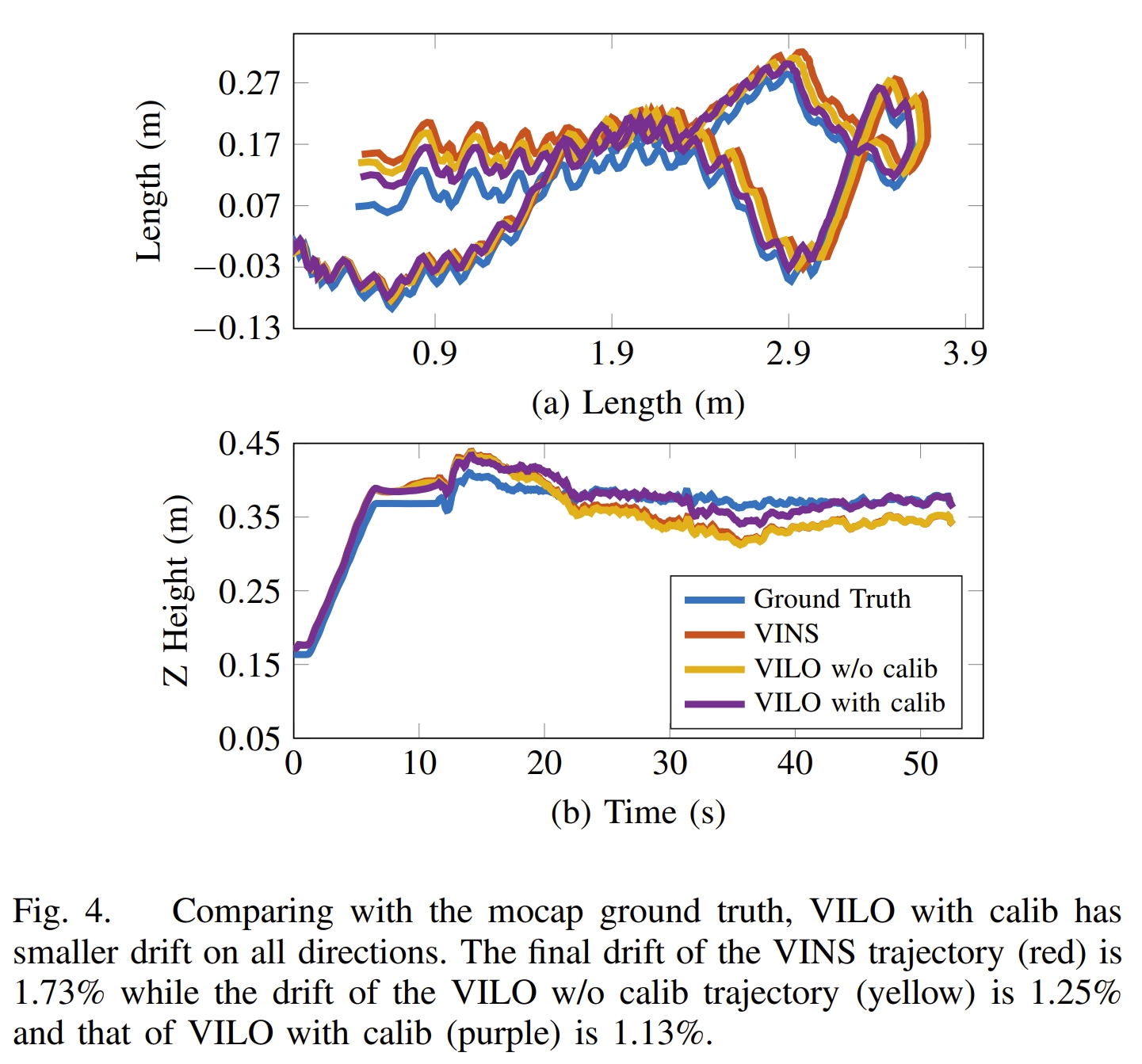
|
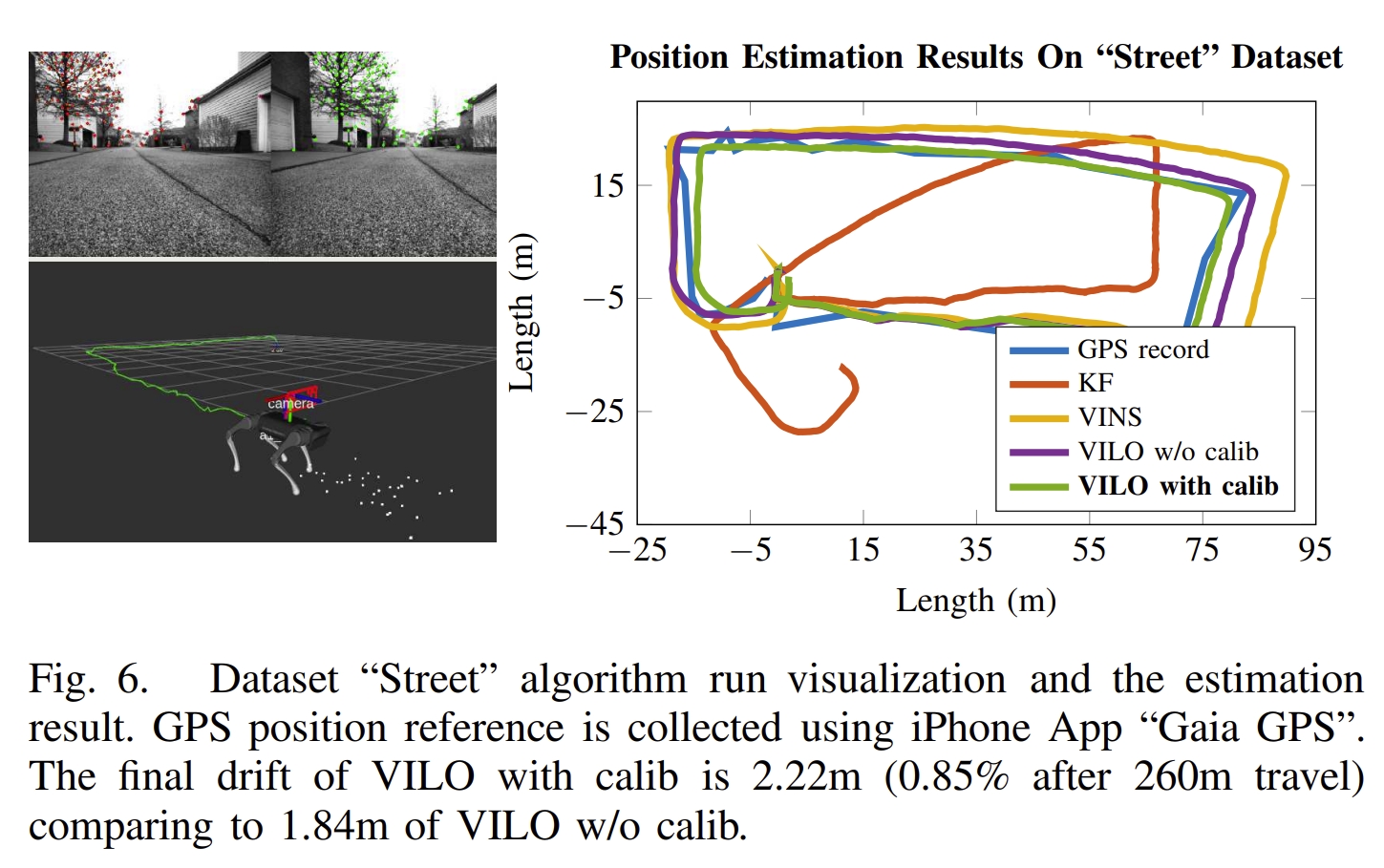
|
VILENS: Visual, Inertial, Lidar, and Leg Odometry for All-Terrain Legged Robots
足式机器人中,对于穿越崎岖地形时,会遇到可变形地形、腿部灵活性和脚部打滑等都会降低状态估计的性能,甚至在短距离内,会存在多步态轨迹无法执行,局部地形重建无法使用等情况。
基于因子图的紧耦合的视觉-IMU-lidar-腿式里程计,并通过对线速度的bias进行在线估计来减少腿式里程计的漂移; 一共2小时,1.8km的实验来验证系统的性能,并且在实验的场景中还包含了松散岩石、斜坡、泥土、滑动、地形形变等挑战;
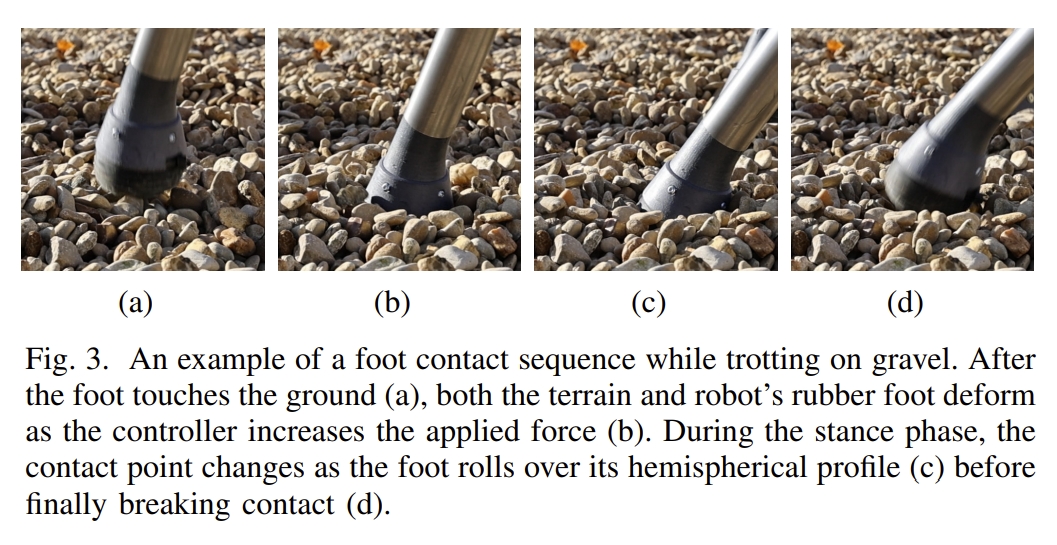
下图比较直观的看到足式机器人在砾石上小跑时脚接触序列的例子。 第一张图是当脚接触地面后,然后就是随着控制器增加施加的力,地形和机器人的橡胶脚都会变形(图2)。 而在站立阶段,第三张图为机械脚在其半球形轮廓上滚动,导致接触点会发生变化,最后一张图则是机械脚准备立刻接触面。
系统的框架如下图所示. 主要包括IMU及运动学的预积分、camera特征跟踪(用的时FAST corner以及KLT),lidar的特征跟踪及ICP匹配,最后就是融合前面因子的图优化框架;
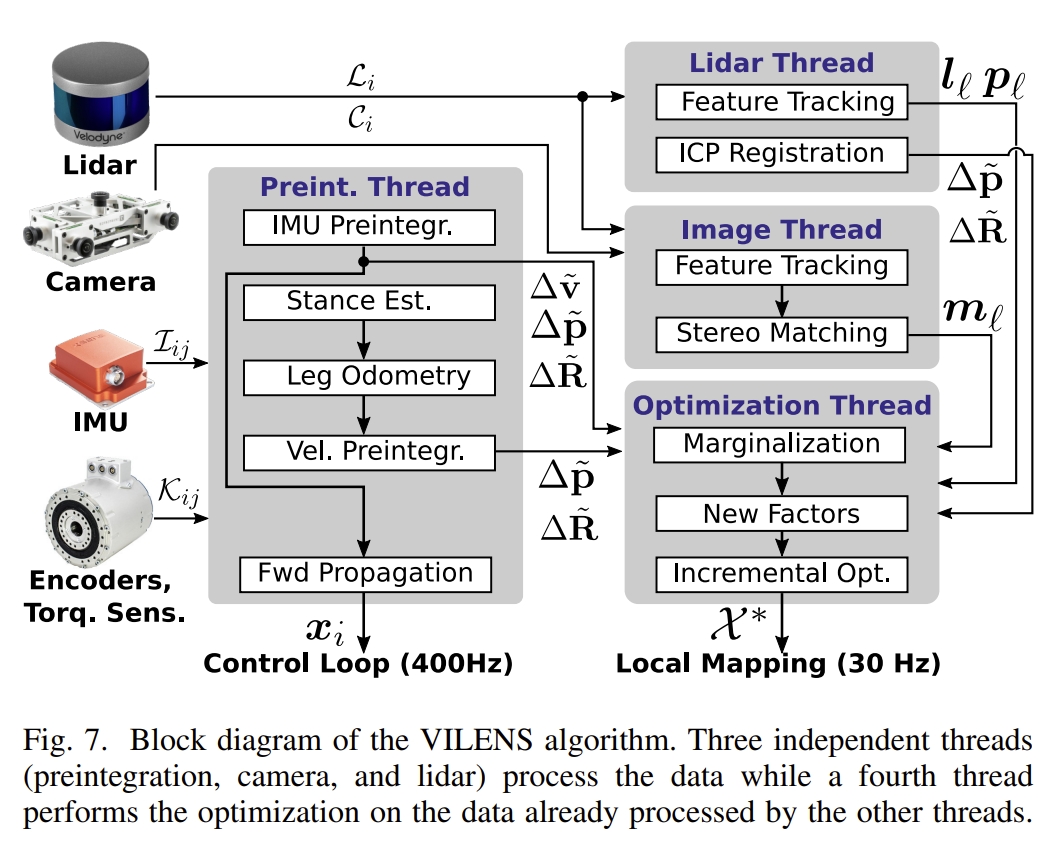
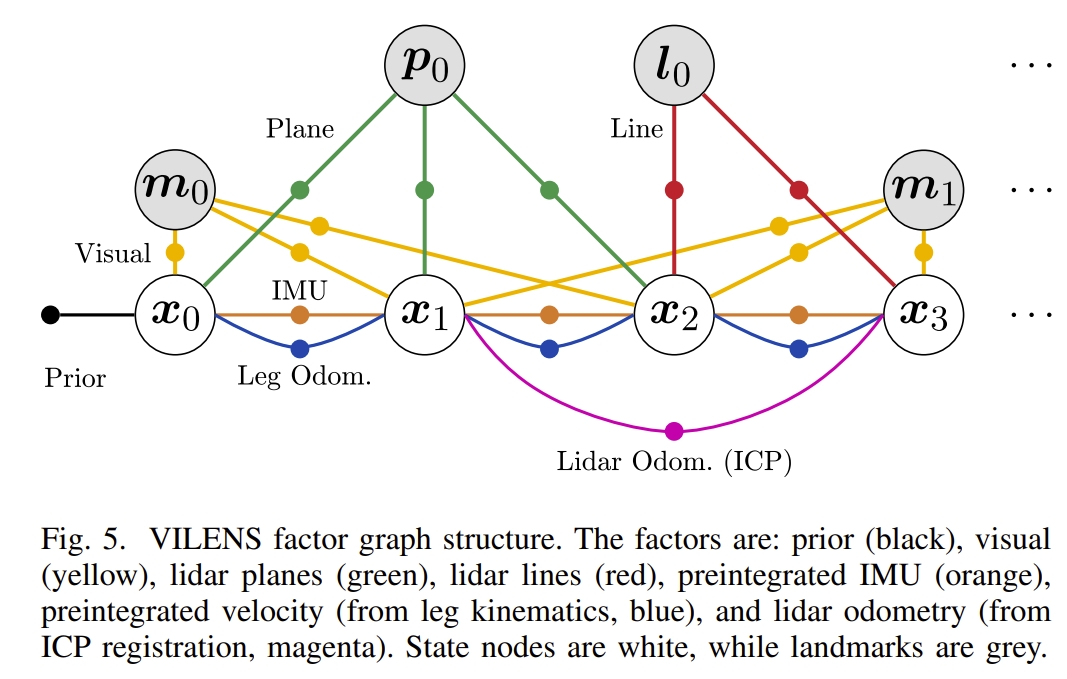
所采用的因子图结构如下图所示
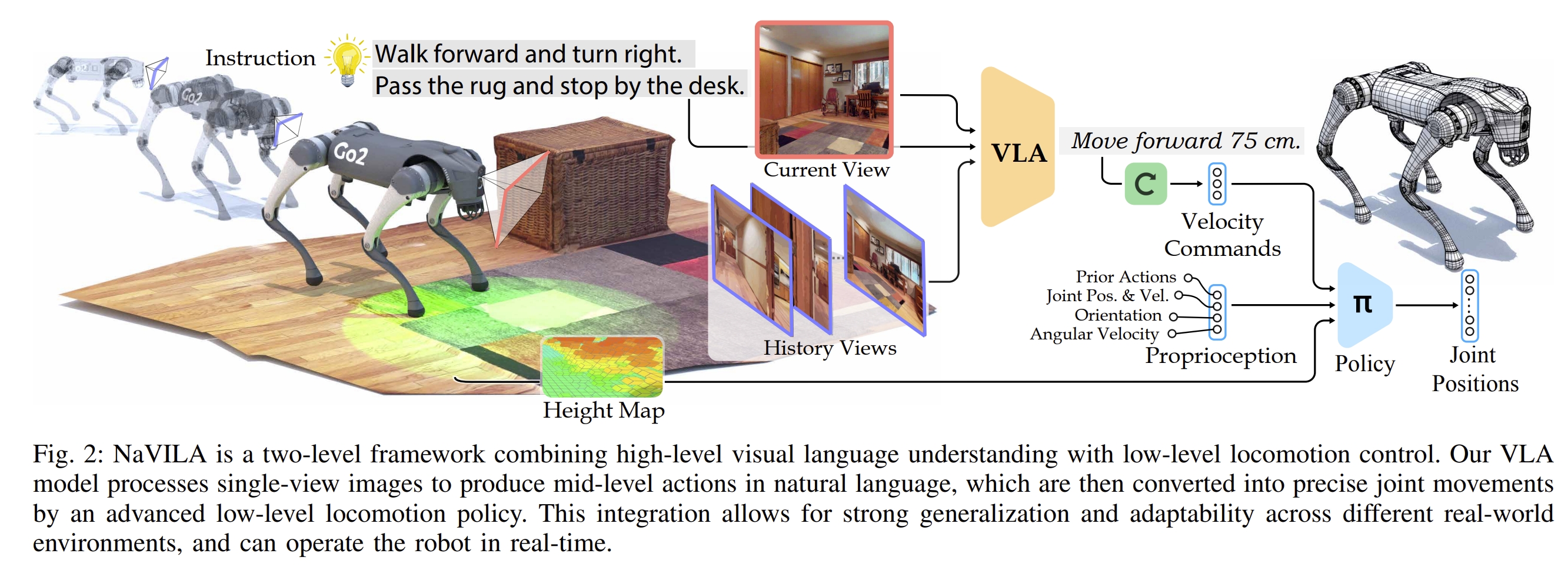
NaVILA: Legged Robot Vision-Language-Action Model for Navigation
该工作实现了腿式机器人的视觉语音导航,即输入人类的指令,通过vision-language model(VLA)来处理RGB图像帧以及结合对应的locomotion skills,机器人即可直接执行任务指令。 将人类语言指令直接转换为底层的腿关节运动。就是让机器人跟随着人的语音指令执行任务,当然还包含了实时运行的locomotion policy,这样两个结合让机器人可以共同完成任务。
作者在人形及四足机器狗上做了大量的实验来验证

其架构如下所示:
Contact-aided invariant extended Kalman filtering for robot state estimation
该工作是针对腿式接触器辅助的基于不变扩展卡尔曼滤波的状态估计器,利用接触器与IMU来对前向的运动学进行校正,进而估算姿态与速度信息。 这篇工作的数学推导比较多,后面对leg odomerty相关深入研究的时候在深入学习与推导吧~
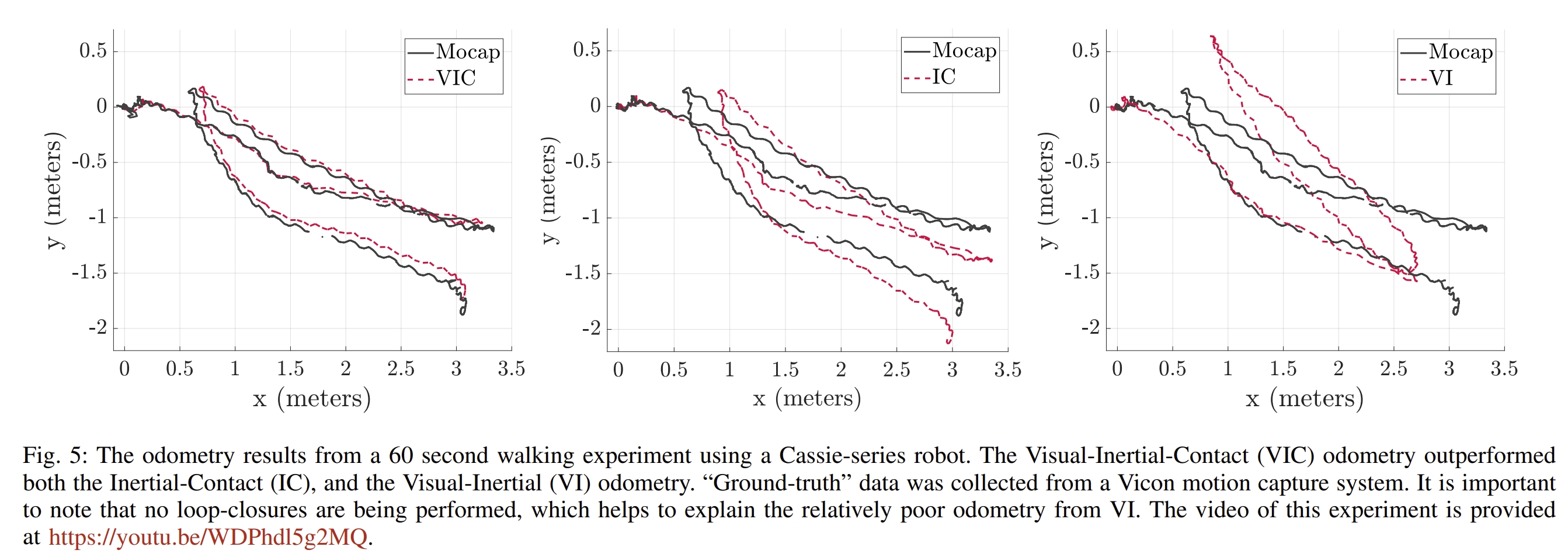
Hybrid contact preintegration for visual-inertial-contact state estimation using factor graphs
该工作提出了基于图优化框架的视觉、imu、关键编码器和腿式接触传感器融合定位系统。 IMU部分采用预计分构建的因子,视觉里程计采用的是SVO2。 至于腿式接触传感器则是开发了一种通过任意数量的接触来实现预积分接触信息的方法。这样以预积分的形式加入因子图中可以减少优化的变量。
实验效果如下图所示(从youtube视频来看感觉是做了个比较简单的实验验证,当然在18年的时候有这样的硬件搭建这样的测试平台已经很不容易了hh)
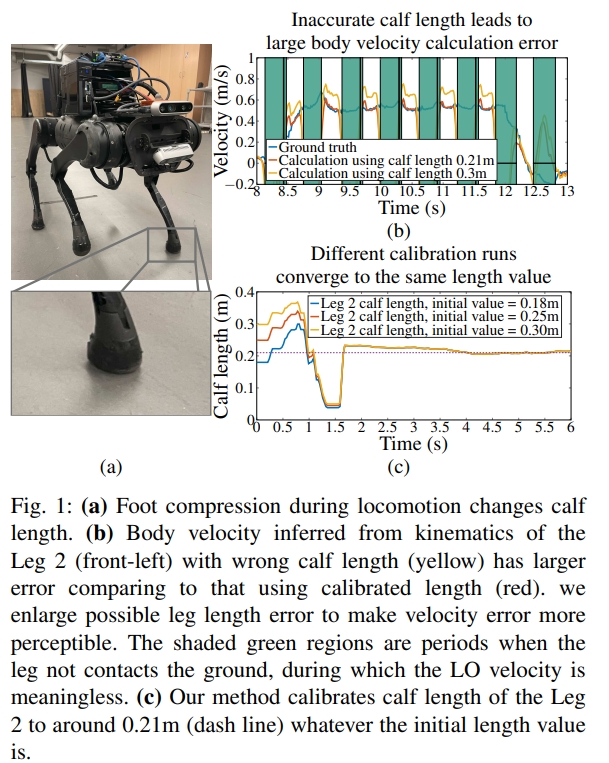
Online Kinematic Calibration for Legged Robots
该工作是在线校正腿式机器人的运动学参数。一般这些运动学参数都是来源于joint encoders, foot contact sensors,以及IMU,通过这些传感器来估算机器人的速度。而估算的速度进一步的跟外部传感器相结合,进而实现运动参数的更新,而更新的过程可以采用滤波或者图优化的方式(分别采用了VINS-mono和ekf-VIO)。
此外,本文还着重于步长的估计。一般步长都是预定义或者手动测量的,但是这会导致很大的误差。每个关键点的一点误差都会导致累积误差(时间与空间维度)。